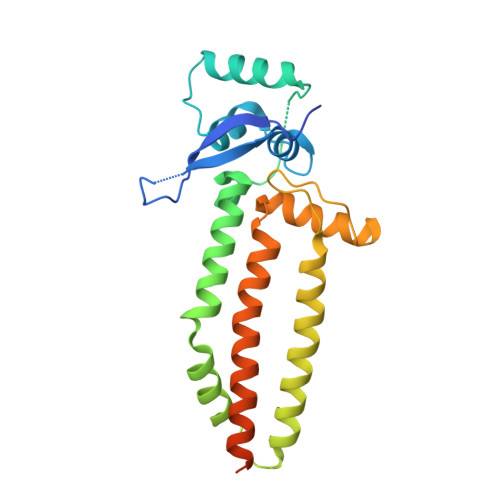
Structural basis for specific DNA sequence motif recognition by the TFAP2 transcription factors.
Liu, K., Xiao, Y., Gan, L., Li, W., Zhang, J., Min, J.(2023) Nucleic Acids Res 51: 8270-8282
- PubMed: 37409559
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkad583
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8J0K, 8J0L, 8J0Q, 8J0R - PubMed Abstract:
The TFAP2 family regulates gene expression during differentiation, development, and organogenesis, and includes five homologs in humans. They all possess a highly conserved DNA binding domain (DBD) followed by a helix-span-helix (HSH) domain. The DBD-HSH tandem domain specifically binds to a GCC(N3)GGC consensus sequence, but the precise recognition mechanisms remain unclear. Here, we found that TFAP2 preferred binding to the GCC(N3)GGC sequence, and the pseudo-palindromic GCC and GGC motifs and the length of the central spacer between the two motifs determined their binding specificity. Structural studies revealed that the two flat amphipathic α-helical HSH domains of TFAP2A stacked with each other to form a dimer via hydrophobic interactions, while the stabilized loops from both DBD domains inserted into two neighboring major grooves of the DNA duplex to form base-specific interactions. This specific DNA binding mechanism controlled the length of the central spacer and determined the DNA sequence specificity of TFAP2. Mutations of the TFAP2 proteins are implicated in various diseases. We illustrated that reduction or disruption of the DNA binding ability of the TFAP2 proteins is the primary cause of TFAP2 mutation-associated diseases. Thus, our findings also offer valuable insights into the pathogenesis of disease-associated mutations in TFAP2 proteins.
- Hubei Key Laboratory of Genetic Regulation and Integrative Biology, School of Life Sciences, Central China Normal University, Wuhan 430079, PR China.
Organizational Affiliation: