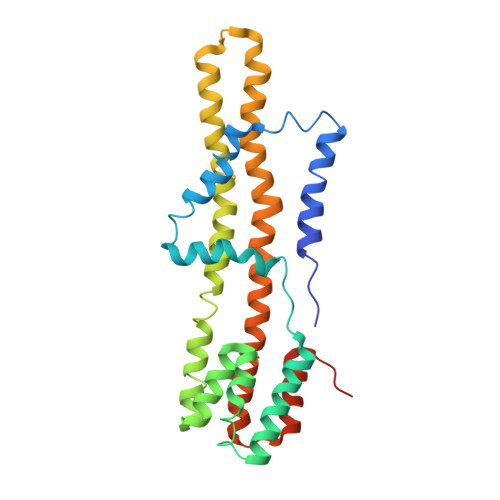
Structure of MotA, a flagellar stator protein, from hyperthermophile.
Nishikino, T., Takekawa, N., Tran, D.P., Kishikawa, J.I., Hirose, M., Onoe, S., Kojima, S., Homma, M., Kitao, A., Kato, T., Imada, K.(2022) Biochem Biophys Res Commun 631: 78-85
- PubMed: 36179499
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2022.09.072
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8GQY - PubMed Abstract:
Many motile bacteria swim and swarm toward favorable environments using the flagellum, which is rotated by a motor embedded in the inner membrane. The motor is composed of the rotor and the stator, and the motor torque is generated by the change of the interaction between the rotor and the stator induced by the ion flow through the stator. A stator unit consists of two types of membrane proteins termed A and B. Recent cryo-EM studies on the stators from mesophiles revealed that the stator consists of five A and two B subunits, whereas the low-resolution EM analysis showed that purified hyperthermophilic MotA forms a tetramer. To clarify the assembly formation and factors enhancing thermostability of the hyperthermophilic stator, we determined the cryo-EM structure of MotA from Aquifex aeolicus (Aa-MotA), a hyperthermophilic bacterium, at 3.42 Å resolution. Aa-MotA forms a pentamer with pseudo C5 symmetry. A simulated model of the Aa-MotA 5 MotB 2 stator complex resembles the structures of mesophilic stator complexes, suggesting that Aa-MotA can assemble into a pentamer equivalent to the stator complex without MotB. The distribution of hydrophobic residues of MotA pentamers suggests that the extremely hydrophobic nature in the subunit boundary and the transmembrane region is a key factor to stabilize hyperthermophilic Aa-MotA.
- Institute for Protein Research, Osaka University, 3-2 Yamadaoka, Suita, Osaka, 565-0871, Japan. Electronic address: nishikino.tatsuro@protein.osaka-u.ac.jp.
Organizational Affiliation: