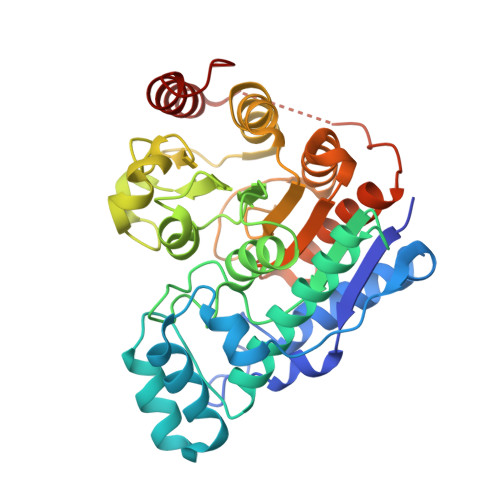
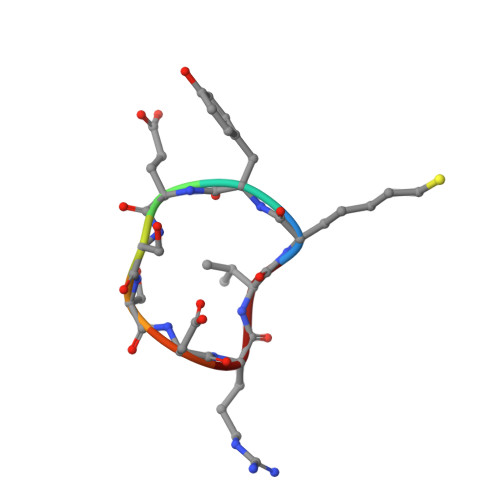
Macrocyclic Octapeptide Binding and Inferences on Protein Substrate Binding to Histone Deacetylase 6.
Watson, P.R., Gupta, S., Hosseinzadeh, P., Brown, B.P., Baker, D., Christianson, D.W.(2023) ACS Chem Biol 18: 959-968
- PubMed: 37027789
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acschembio.3c00113
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8EQI - PubMed Abstract:
Histone deacetylases (HDACs) are essential for the regulation of myriad biological processes, and their aberrant function is implicated in cancer, neurodegeneration, and other diseases. The cytosolic isozyme HDAC6 is unique among the greater family of deacetylases in that it contains two catalytic domains, CD1 and CD2. HDAC6 CD2 is responsible for tubulin deacetylase and tau deacetylase activities, inhibition of which is a key goal as new therapeutic approaches are explored. Of particular interest as HDAC inhibitors are naturally occurring cyclic tetrapeptides such as Trapoxin A or HC Toxin, or the cyclic depsipeptides Largazole and Romidepsin. Even more intriguing are larger, computationally designed macrocyclic peptide inhibitors. Here, we report the 2.0 Å resolution crystal structure of HDAC6 CD2 complexed with macrocyclic octapeptide 1 . Comparison with the previously reported structure of the complex with macrocyclic octapeptide 2 reveals that a potent thiolate-zinc interaction made by the unnatural amino acid ( S )-2-amino-7-sulfanylheptanoic acid contributes to nanomolar inhibitory potency for each inhibitor. Apart from this zinc-binding residue, octapeptides adopt strikingly different overall conformations and make few direct hydrogen bonds with the protein. Intermolecular interactions are dominated by water-mediated hydrogen bonds; in essence, water molecules appear to cushion the enzyme-octapeptide interface. In view of the broad specificity observed for protein substrates of HDAC6 CD2, we suggest that the binding of macrocyclic octapeptides may mimic certain features of the binding of macromolecular protein substrates.
- Roy and Diana Vagelos Laboratories, Department of Chemistry, University of Pennsylvania, 231 South 34th Street, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania 19104-6323, United States.
Organizational Affiliation: