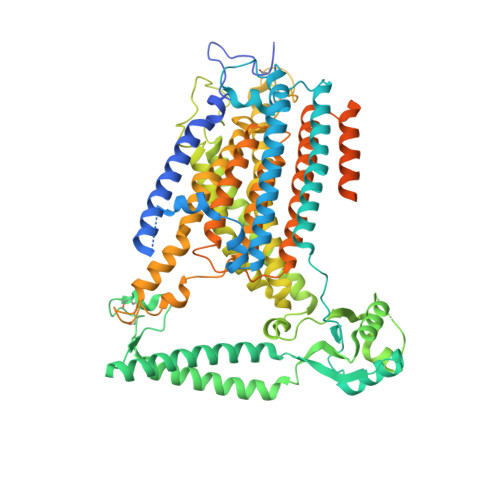
TMEM63 proteins function as monomeric high-threshold mechanosensitive ion channels.
Zheng, W., Rawson, S., Shen, Z., Tamilselvan, E., Smith, H.E., Halford, J., Shen, C., Murthy, S.E., Ulbrich, M.H., Sotomayor, M., Fu, T.M., Holt, J.R.(2023) Neuron 111: 3195
- PubMed: 37543036
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2023.07.006
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8EHW, 8EHX - PubMed Abstract:
OSCA/TMEM63s form mechanically activated (MA) ion channels in plants and animals, respectively. OSCAs and related TMEM16s and transmembrane channel-like (TMC) proteins form homodimers with two pores. Here, we uncover an unanticipated monomeric configuration of TMEM63 proteins. Structures of TMEM63A and TMEM63B (referred to as TMEM63s) revealed a single highly restricted pore. Functional analyses demonstrated that TMEM63s are bona fide mechanosensitive ion channels, characterized by small conductance and high thresholds. TMEM63s possess evolutionary variations in the intracellular linker IL2, which mediates dimerization in OSCAs. Replacement of OSCA1.2 IL2 with TMEM63A IL2 or mutations to key variable residues resulted in monomeric OSCA1.2 and MA currents with significantly higher thresholds. Structural analyses revealed substantial conformational differences in the mechano-sensing domain IL2 and gating helix TM6 between TMEM63s and OSCA1.2. Our studies reveal that mechanosensitivity in OSCA/TMEM63 channels is affected by oligomerization and suggest gating mechanisms that may be shared by OSCA/TMEM63, TMEM16, and TMC channels.
- Departments of Otolaryngology & Neurology, Boston Children's Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA 02115, USA. Electronic address: wang.zheng@childrens.harvard.edu.
Organizational Affiliation: