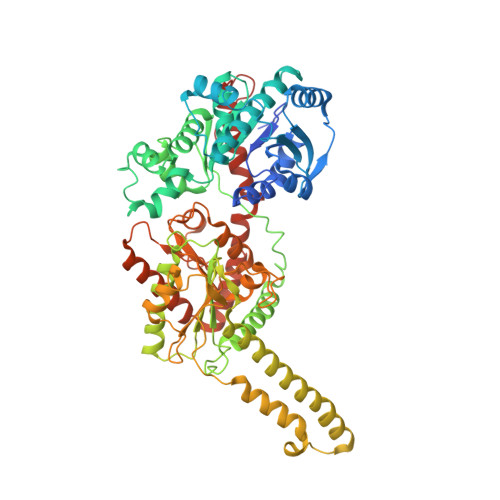
The structural mechanism of human glycogen synthesis by the GYS1-GYG1 complex.
Fastman, N.M., Liu, Y., Ramanan, V., Merritt, H., Ambing, E., DePaoli-Roach, A.A., Roach, P.J., Hurley, T.D., Mellem, K.T., Ullman, J.C., Green, E., Morgans Jr., D., Tzitzilonis, C.(2022) Cell Rep 40: 111041-111041
- PubMed: 35793618
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2022.111041
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8CVX, 8CVY, 8CVZ - PubMed Abstract:
Glycogen is the primary energy reserve in mammals, and dysregulation of glycogen metabolism can result in glycogen storage diseases (GSDs). In muscle, glycogen synthesis is initiated by the enzymes glycogenin-1 (GYG1), which seeds the molecule by autoglucosylation, and glycogen synthase-1 (GYS1), which extends the glycogen chain. Although both enzymes are required for proper glycogen production, the nature of their interaction has been enigmatic. Here, we present the human GYS1:GYG1 complex in multiple conformations representing different functional states. We observe an asymmetric conformation of GYS1 that exposes an interface for close GYG1 association, and propose this state facilitates handoff of the GYG1-associated glycogen chain to a GYS1 subunit for elongation. Full activation of GYS1 widens the GYG1-binding groove, enabling GYG1 release concomitant with glycogen chain growth. This structural mechanism connecting chain nucleation and extension explains the apparent stepwise nature of glycogen synthesis and suggests distinct states to target for GSD-modifying therapeutics.
- Maze Therapeutics, 171 Oyster Point Blvd, Suite 300, South San Francisco, CA 94080, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: