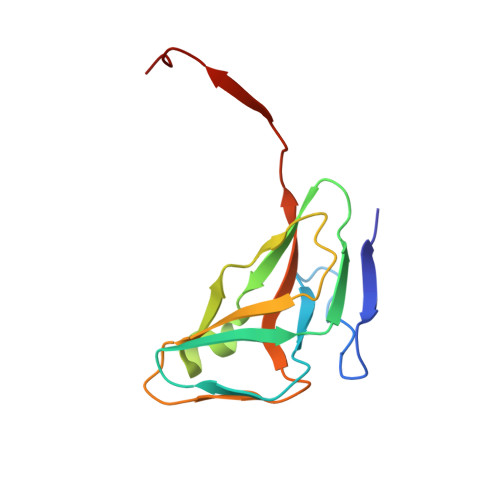
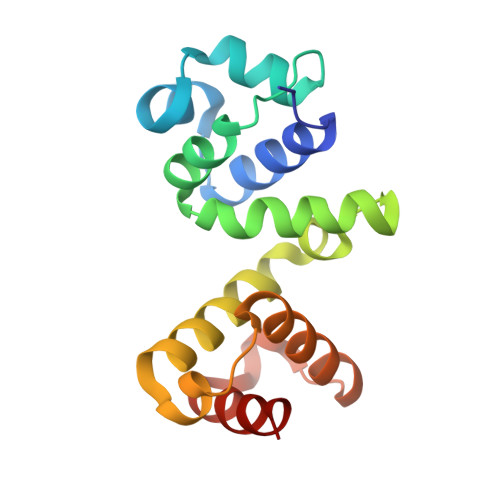
Full-length inhibitor protein is the most effective to perturb human dUTPase activity.
Kohegyi, B., Toth, Z.S., Gal, E., Laczkovich, M., Benedek, A., Vertessy, B.G., Nyiri, K.(2025) Sci Rep 15: 4836-4836
- PubMed: 39924564
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-025-86131-7
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8C8I - PubMed Abstract:
It has been demonstrated recently that knockout of the dUTPase enzyme leads to early embryonic lethality in mice. However, to explore the physiological processes arising upon the lack of dUTPase an effective and selective enzyme inhibitor is much needed. A highly specific and strong binding proteinaceous human dUTPase inhibitor described by us recently was a promising starting point to develop a molecular tool to study temporal and conditional dUTPase inhibition in cellulo. Towards this end we determined the 3D crystal structure of the crystallizable amino terminal domain of inhibitor protein, named Stl NT in complex with the human dUTPase and designed several point mutants based on the structure to improve the inhibition effectivity. The effect of Stl NT and a peptide derived from the full-length inhibitor on the activity of the human dUTPase was also tested. We showed that the C-terminal part of the Stl protein omitted from the crystal structure has an important role in the enzyme inhibition as the full-length Stl is needed to exert maximal inhibition on the human dUTPase.
- Department of Applied Biotechnology and Food Science, Faculty of Chemical Technology and Biotechnology, Budapest University of Technology and Economics, Műegyetem rkp. 3, Budapest, 111, Hungary.
Organizational Affiliation: