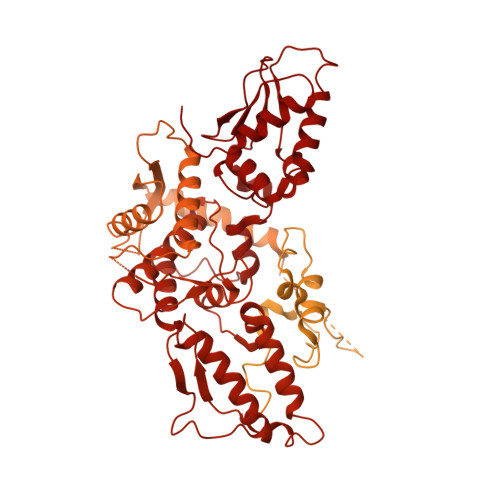
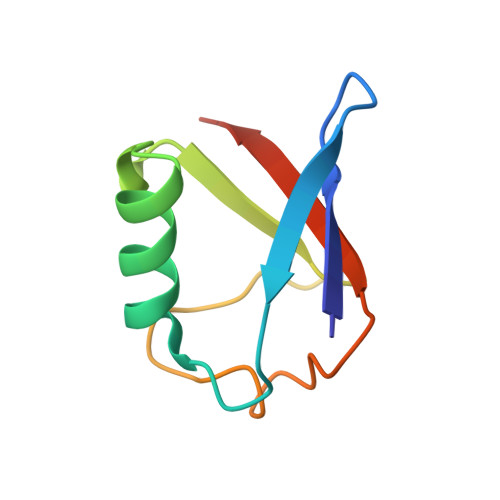
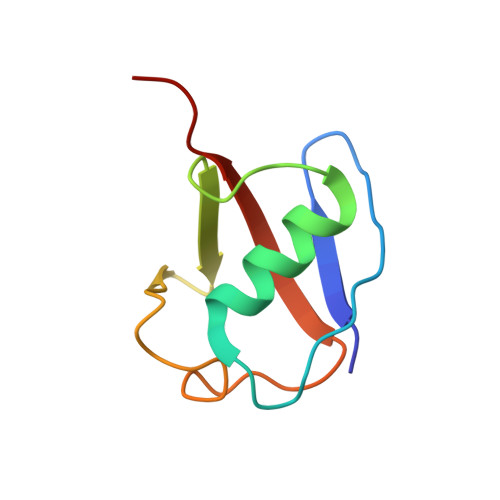
Structural snapshots along K48-linked ubiquitin chain formation by the HECT E3 UBR5.
Hehl, L.A., Horn-Ghetko, D., Prabu, J.R., Vollrath, R., Vu, D.T., Perez Berrocal, D.A., Mulder, M.P.C., van der Heden van Noort, G.J., Schulman, B.A.(2024) Nat Chem Biol 20: 190-200
- PubMed: 37620400
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41589-023-01414-2
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8C06, 8C07 - PubMed Abstract:
Ubiquitin (Ub) chain formation by homologous to E6AP C-terminus (HECT)-family E3 ligases regulates vast biology, yet the structural mechanisms remain unknown. We used chemistry and cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) to visualize stable mimics of the intermediates along K48-linked Ub chain formation by the human E3, UBR5. The structural data reveal a ≈ 620 kDa UBR5 dimer as the functional unit, comprising a scaffold with flexibly tethered Ub-associated (UBA) domains, and elaborately arranged HECT domains. Chains are forged by a UBA domain capturing an acceptor Ub, with its K48 lured into the active site by numerous interactions between the acceptor Ub, manifold UBR5 elements and the donor Ub. The cryo-EM reconstructions allow defining conserved HECT domain conformations catalyzing Ub transfer from E2 to E3 and from E3. Our data show how a full-length E3, ubiquitins to be adjoined, E2 and intermediary products guide a feed-forward HECT domain conformational cycle establishing a highly efficient, broadly targeting, K48-linked Ub chain forging machine.
- Department of Chemistry, School of Natural Sciences, Technical University of Munich, Garching, Germany.
Organizational Affiliation: