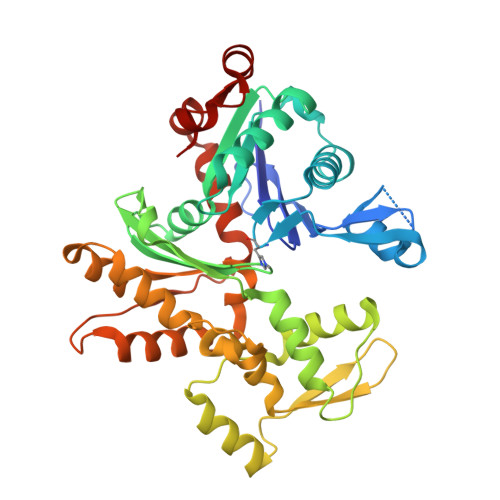
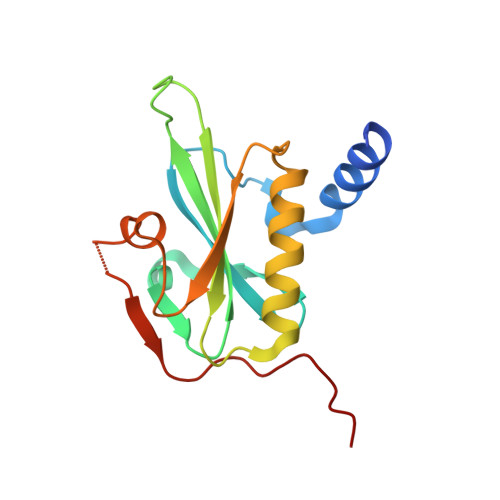
Structures and mechanisms of actin ATP hydrolysis.
Kanematsu, Y., Narita, A., Oda, T., Koike, R., Ota, M., Takano, Y., Moritsugu, K., Fujiwara, I., Tanaka, K., Komatsu, H., Nagae, T., Watanabe, N., Iwasa, M., Maeda, Y., Takeda, S.(2022) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 119: e2122641119-e2122641119
- PubMed: 36252034
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2122641119
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7W4Z, 7W50, 7W51, 7W52, 7YNE - PubMed Abstract:
The major cytoskeleton protein actin undergoes cyclic transitions between the monomeric G-form and the filamentous F-form, which drive organelle transport and cell motility. This mechanical work is driven by the ATPase activity at the catalytic site in the F-form. For deeper understanding of the actin cellular functions, the reaction mechanism must be elucidated. Here, we show that a single actin molecule is trapped in the F-form by fragmin domain-1 binding and present their crystal structures in the ATP analog-, ADP-Pi-, and ADP-bound forms, at 1.15-Å resolutions. The G-to-F conformational transition shifts the side chains of Gln137 and His161, which relocate four water molecules including W1 (attacking water) and W2 (helping water) to facilitate the hydrolysis. By applying quantum mechanics/molecular mechanics calculations to the structures, we have revealed a consistent and comprehensive reaction path of ATP hydrolysis by the F-form actin. The reaction path consists of four steps: 1) W1 and W2 rotations; 2) P G -O 3B bond cleavage; 3) four concomitant events: W1-PO 3 - formation, OH - and proton cleavage, nucleophilic attack by the OH - against P G , and the abstracted proton transfer; and 4) proton relocation that stabilizes the ADP-Pi-bound F-form actin. The mechanism explains the slow rate of ATP hydrolysis by actin and the irreversibility of the hydrolysis reaction. While the catalytic strategy of actin ATP hydrolysis is essentially the same as those of motor proteins like myosin, the process after the hydrolysis is distinct and discussed in terms of Pi release, F-form destabilization, and global conformational changes.
- Graduate School of Information Sciences, Hiroshima City University, Hiroshima 731-3194, Japan.
Organizational Affiliation: