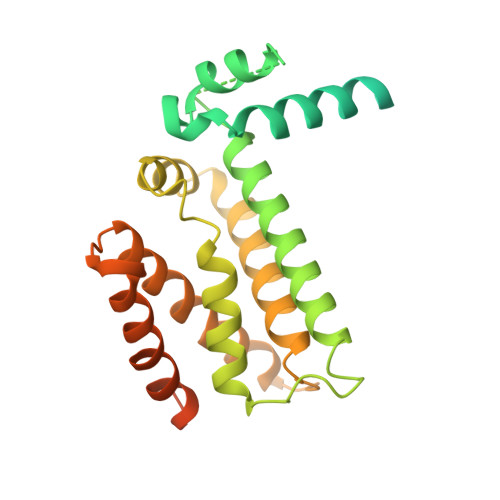
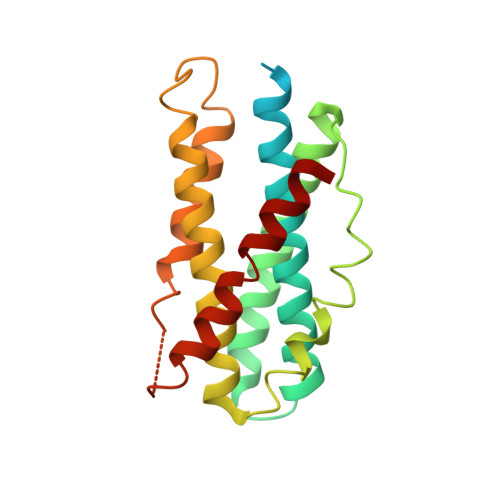
Structure and functionality of a multimeric human COQ7:COQ9 complex.
Manicki, M., Aydin, H., Abriata, L.A., Overmyer, K.A., Guerra, R.M., Coon, J.J., Dal Peraro, M., Frost, A., Pagliarini, D.J.(2022) Mol Cell 82: 4307-4323.e10
- PubMed: 36306796
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2022.10.003
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7SSP, 7SSS - PubMed Abstract:
Coenzyme Q (CoQ) is a redox-active lipid essential for core metabolic pathways and antioxidant defense. CoQ is synthesized upon the mitochondrial inner membrane by an ill-defined "complex Q" metabolon. Here, we present structure-function analyses of a lipid-, substrate-, and NADH-bound complex comprising two complex Q subunits: the hydroxylase COQ7 and the lipid-binding protein COQ9. We reveal that COQ7 adopts a ferritin-like fold with a hydrophobic channel whose substrate-binding capacity is enhanced by COQ9. Using molecular dynamics, we further show that two COQ7:COQ9 heterodimers form a curved tetramer that deforms the membrane, potentially opening a pathway for the CoQ intermediates to translocate from the bilayer to the proteins' lipid-binding sites. Two such tetramers assemble into a soluble octamer with a pseudo-bilayer of lipids captured within. Together, these observations indicate that COQ7 and COQ9 cooperate to access hydrophobic precursors within the membrane and coordinate subsequent synthesis steps toward producing CoQ.
- Department of Cell Biology and Physiology, Washington University School of Medicine, St. Louis, MO 63110, USA; Morgridge Institute for Research, Madison, WI 53715, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: