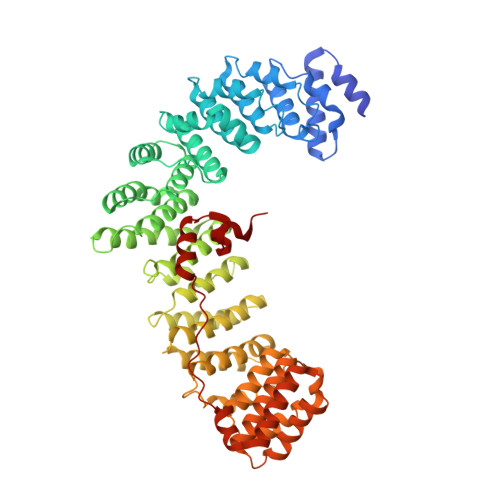
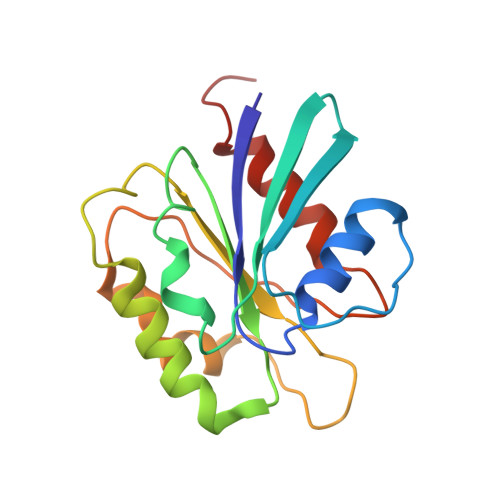
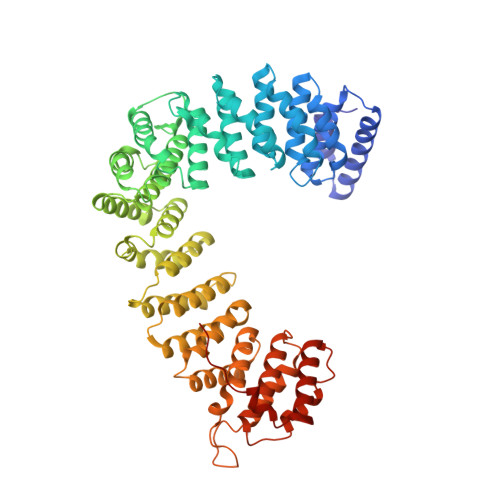
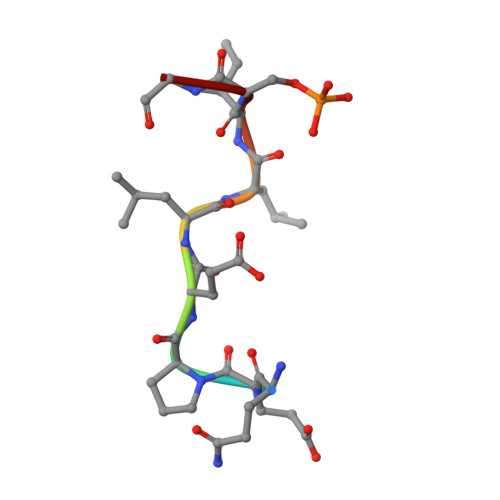
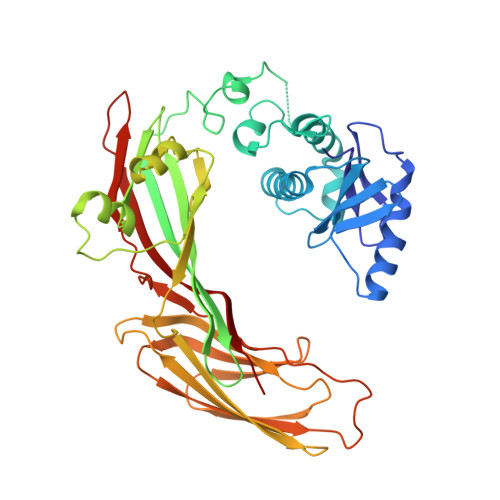
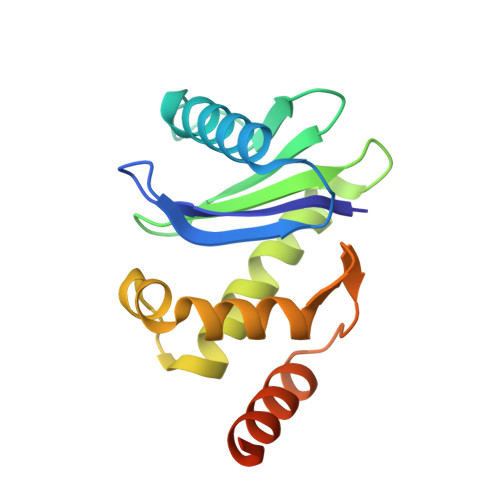
Clathrin-associated AP-1 controls termination of STING signalling.
Liu, Y., Xu, P., Rivara, S., Liu, C., Ricci, J., Ren, X., Hurley, J.H., Ablasser, A.(2022) Nature 610: 761-767
- PubMed: 36261523
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-022-05354-0
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7R4H - PubMed Abstract:
Stimulator of interferon genes (STING) functions downstream of cyclic GMP-AMP synthase in DNA sensing or as a direct receptor for bacterial cyclic dinucleotides and small molecules to activate immunity during infection, cancer and immunotherapy 1-10 . Precise regulation of STING is essential to ensure balanced immune responses and prevent detrimental autoinflammation 11-16 . After activation, STING, a transmembrane protein, traffics from the endoplasmic reticulum to the Golgi, where its phosphorylation by the protein kinase TBK1 enables signal transduction 17-20 . The mechanism that ends STING signalling at the Golgi remains unknown. Here we show that adaptor protein complex 1 (AP-1) controls the termination of STING-dependent immune activation. We find that AP-1 sorts phosphorylated STING into clathrin-coated transport vesicles for delivery to the endolysosomal system, where STING is degraded 21 . We identify a highly conserved dileucine motif in the cytosolic C-terminal tail (CTT) of STING that, together with TBK1-dependent CTT phosphorylation, dictates the AP-1 engagement of STING. A cryo-electron microscopy structure of AP-1 in complex with phosphorylated STING explains the enhanced recognition of TBK1-activated STING. We show that suppression of AP-1 exacerbates STING-induced immune responses. Our results reveal a structural mechanism of negative regulation of STING and establish that the initiation of signalling is inextricably associated with its termination to enable transient activation of immunity.
- Global Health Institute, Swiss Federal Institute of Technology Lausanne (EPFL), Lausanne, Switzerland.
Organizational Affiliation: