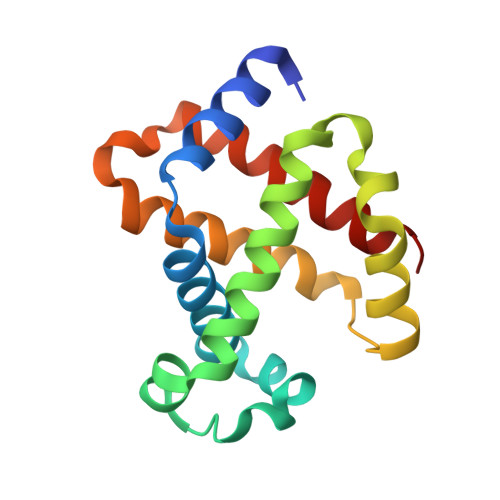
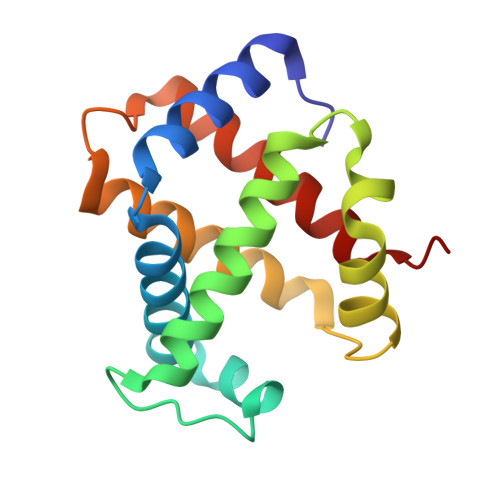
Structural and oxidative investigation of a recombinant high-yielding fetal hemoglobin mutant.
Kettisen, K., Nyblom, M., Smeds, E., Fago, A., Bulow, L.(2023) Front Mol Biosci 10: 1133985-1133985
- PubMed: 37006610
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3389/fmolb.2023.1133985
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7QU4 - PubMed Abstract:
Human fetal hemoglobin (HbF) is an attractive starting protein for developing an effective agent for oxygen therapeutics applications. This requires that HbF can be produced in heterologous systems at high levels and in a homogeneous form. The introduction of negative charges on the surface of the α-chain in HbF can enhance the recombinant production yield of a functional protein in Escherichia coli . In this study, we characterized the structural, biophysical, and biological properties of an HbF mutant carrying four additional negative charges on each α-chain (rHbFα4). The 3D structure of the rHbFα4 mutant was solved with X-ray crystallography at 1.6 Å resolution. Apart from enabling a higher yield in recombinant protein production in E. coli , we observed that the normal DNA cleavage activity of the HbF was significantly lowered, with a four-time reduced rate constant for the rHbFα4 mutant. The oxygen-binding properties of the rHbFα4 mutant were identical to the wild-type protein. No significant difference between the wild-type and rHbFα4 was observed for the investigated oxidation rates (autoxidation and H 2 O 2 -mediated ferryl formation). However, the ferryl reduction reaction indicated some differences, which appear to be related to the reaction rates linked to the α-chain.
- Pure and Applied Biochemistry, Department of Chemistry, Lund University, Lund, Sweden.
Organizational Affiliation: