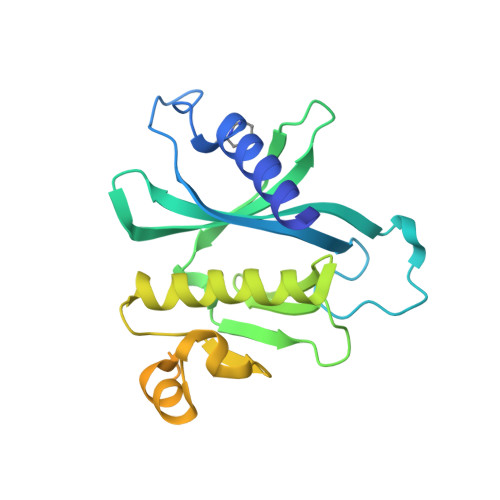
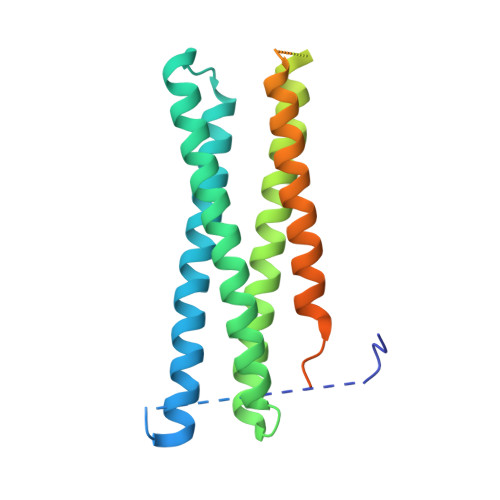
Double NPY motifs at the N-terminus of the yeast t-SNARE Sso2 synergistically bind Sec3 to promote membrane fusion.
Peer, M., Yuan, H., Zhang, Y., Korbula, K., Novick, P., Dong, G.(2022) Elife 11
- PubMed: 35979953
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.82041
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7Q83 - PubMed Abstract:
Exocytosis is an active vesicle trafficking process by which eukaryotes secrete materials to the extracellular environment and insert membrane proteins into the plasma membrane. The final step of exocytosis in yeast involves the assembly of two t-SNAREs, Sso1/2 and Sec9, with the v-SNARE, Snc1/2, on secretory vesicles. The rate-limiting step in this process is the formation of a binary complex of the two t-SNAREs. Despite a previous report of acceleration of binary complex assembly by Sec3, it remains unknown how Sso2 is efficiently recruited to the vesicle-docking site marked by Sec3. Here, we report a crystal structure of the pleckstrin homology (PH) domain of Sec3 in complex with a nearly full-length version of Sso2 lacking only its C-terminal transmembrane helix. The structure shows a previously uncharacterized binding site for Sec3 at the N-terminus of Sso2, consisting of two highly conserved triple residue motifs (NPY: Asn-Pro-Tyr). We further reveal that the two NPY motifs bind Sec3 synergistically, which together with the previously reported binding interface constitute dual-site interactions between Sso2 and Sec3 to drive the fusion of secretory vesicles at target sites on the plasma membrane.
- Max Perutz Labs, Vienna Biocenter, Medical University of Vienna, Vienna, Austria.
Organizational Affiliation: