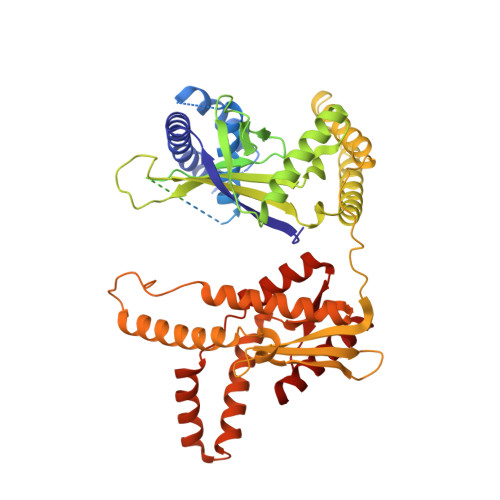
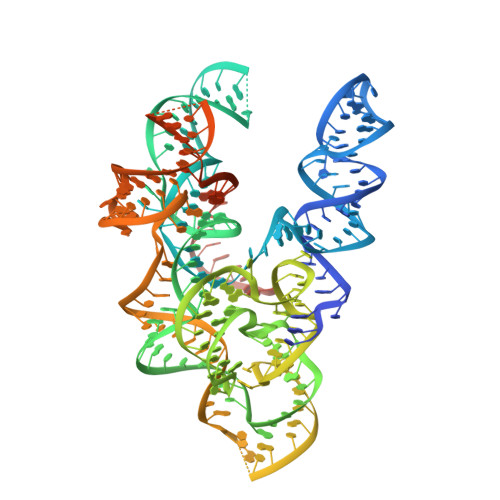
Target site selection and remodelling by type V CRISPR-transposon systems.
Querques, I., Schmitz, M., Oberli, S., Chanez, C., Jinek, M.(2021) Nature 599: 497-502
- PubMed: 34759315
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-021-04030-z
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7OXD, 7PLA, 7PLH, 9GO0 - PubMed Abstract:
Canonical CRISPR-Cas systems provide adaptive immunity against mobile genetic elements 1 . However, type I-F, I-B and V-K systems have been adopted by Tn7-like transposons to direct RNA-guided transposon insertion 2-7 . Type V-K CRISPR-associated transposons rely on the pseudonuclease Cas12k, the transposase TnsB, the AAA+ ATPase TnsC and the zinc-finger protein TniQ 7 , but the molecular mechanism of RNA-directed DNA transposition has remained elusive. Here we report cryo-electron microscopic structures of a Cas12k-guide RNA-target DNA complex and a DNA-bound, polymeric TnsC filament from the CRISPR-associated transposon system of the photosynthetic cyanobacterium Scytonema hofmanni. The Cas12k complex structure reveals an intricate guide RNA architecture and critical interactions mediating RNA-guided target DNA recognition. TnsC helical filament assembly is ATP-dependent and accompanied by structural remodelling of the bound DNA duplex. In vivo transposition assays corroborate key features of the structures, and biochemical experiments show that TniQ restricts TnsC polymerization, while TnsB interacts directly with TnsC filaments to trigger their disassembly upon ATP hydrolysis. Together, these results suggest that RNA-directed target selection by Cas12k primes TnsC polymerization and DNA remodelling, generating a recruitment platform for TnsB to catalyse site-specific transposon insertion. Insights from this work will inform the development of CRISPR-associated transposons as programmable site-specific gene insertion tools.
- Department of Biochemistry, University of Zurich, Zurich, Switzerland.
Organizational Affiliation: