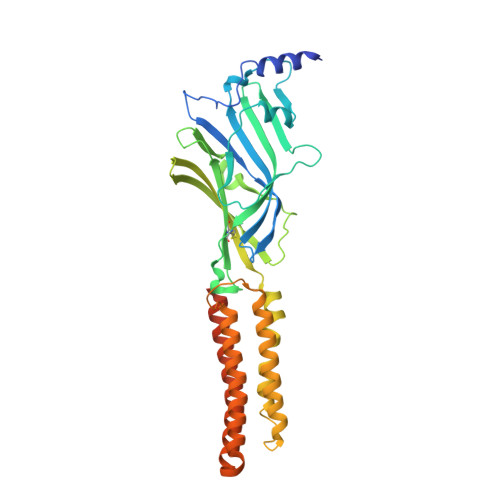
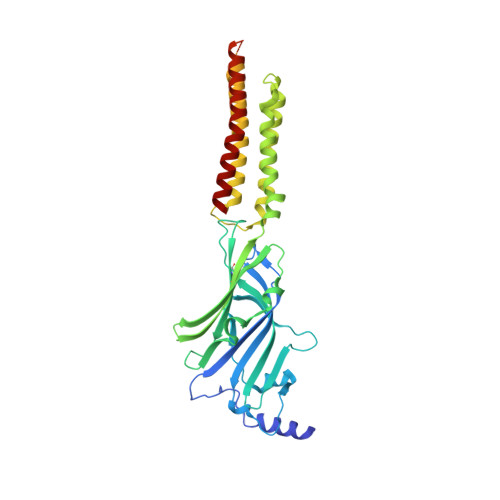
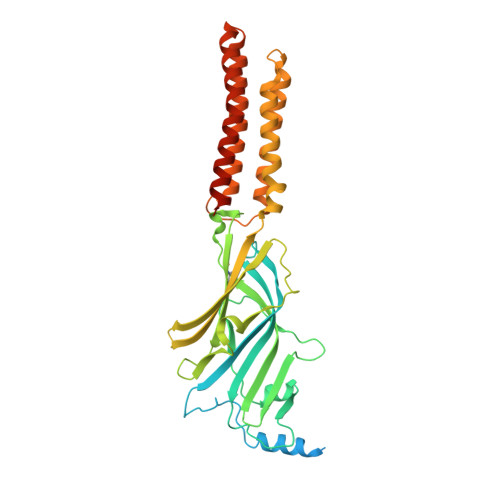
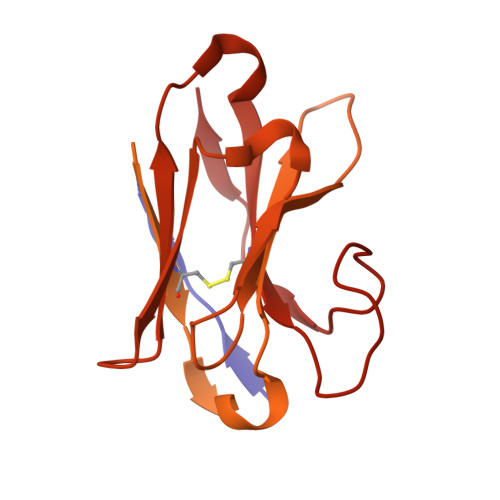
Mechanisms of inhibition and activation of extrasynaptic alpha beta GABA A receptors.
Kasaragod, V.B., Mortensen, M., Hardwick, S.W., Wahid, A.A., Dorovykh, V., Chirgadze, D.Y., Smart, T.G., Miller, P.S.(2022) Nature 602: 529-533
- PubMed: 35140402
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-022-04402-z
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7PBD, 7PBZ, 7PC0 - PubMed Abstract:
Type A GABA (γ-aminobutyric acid) receptors represent a diverse population in the mammalian brain, forming pentamers from combinations of α-, β-, γ-, δ-, ε-, ρ-, θ- and π-subunits 1 . αβ, α4βδ, α6βδ and α5βγ receptors favour extrasynaptic localization, and mediate an essential persistent (tonic) inhibitory conductance in many regions of the mammalian brain 1,2 . Mutations of these receptors in humans are linked to epilepsy and insomnia 3,4 . Altered extrasynaptic receptor function is implicated in insomnia, stroke and Angelman and Fragile X syndromes 1,5 , and drugs targeting these receptors are used to treat postpartum depression 6 . Tonic GABAergic responses are moderated to avoid excessive suppression of neuronal communication, and can exhibit high sensitivity to Zn 2+ blockade, in contrast to synapse-preferring α1βγ, α2βγ and α3βγ receptor responses 5,7-12 . Here, to resolve these distinctive features, we determined structures of the predominantly extrasynaptic αβ GABA A receptor class. An inhibited state bound by both the lethal paralysing agent α-cobratoxin 13 and Zn 2+ was used in comparisons with GABA-Zn 2+ and GABA-bound structures. Zn 2+ nullifies the GABA response by non-competitively plugging the extracellular end of the pore to block chloride conductance. In the absence of Zn 2+ , the GABA signalling response initially follows the canonical route until it reaches the pore. In contrast to synaptic GABA A receptors, expansion of the midway pore activation gate is limited and it remains closed, reflecting the intrinsic low efficacy that characterizes the extrasynaptic receptor. Overall, this study explains distinct traits adopted by αβ receptors that adapt them to a role in tonic signalling.
- Department of Pharmacology, University of Cambridge, Cambridge, UK.
Organizational Affiliation: