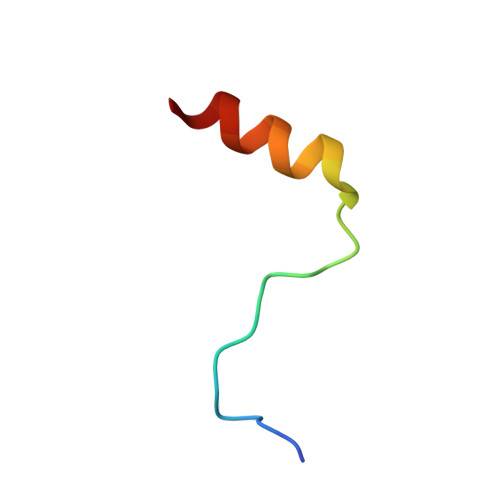
A Concerted Action of UBA5 C-Terminal Unstructured Regions Is Important for Transfer of Activated UFM1 to UFC1.
Wesch, N., Lohr, F., Rogova, N., Dotsch, V., Rogov, V.V.(2021) Int J Mol Sci 22
- PubMed: 34299007
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22147390
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7OVC - PubMed Abstract:
Ubiquitin fold modifier 1 (UFM1) is a member of the ubiquitin-like protein family. UFM1 undergoes a cascade of enzymatic reactions including activation by UBA5 (E1), transfer to UFC1 (E2) and selective conjugation to a number of target proteins via UFL1 (E3) enzymes. Despite the importance of ufmylation in a variety of cellular processes and its role in the pathogenicity of many human diseases, the molecular mechanisms of the ufmylation cascade remains unclear. In this study we focused on the biophysical and biochemical characterization of the interaction between UBA5 and UFC1. We explored the hypothesis that the unstructured C-terminal region of UBA5 serves as a regulatory region, controlling cellular localization of the elements of the ufmylation cascade and effective interaction between them. We found that the last 20 residues in UBA5 are pivotal for binding to UFC1 and can accelerate the transfer of UFM1 to UFC1. We solved the structure of a complex of UFC1 and a peptide spanning the last 20 residues of UBA5 by NMR spectroscopy. This structure in combination with additional NMR titration and isothermal titration calorimetry experiments revealed the mechanism of interaction and confirmed the importance of the C-terminal unstructured region in UBA5 for the ufmylation cascade.
- Institute of Biophysical Chemistry, Center for Biomolecular Magnetic Resonance, Goethe-University Frankfurt, 60438 Frankfurt am Main, Germany.
Organizational Affiliation: