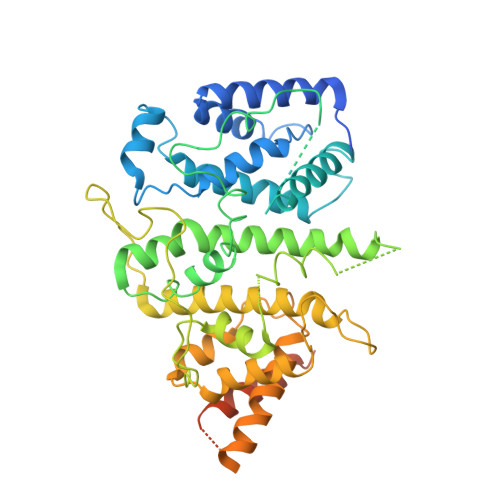
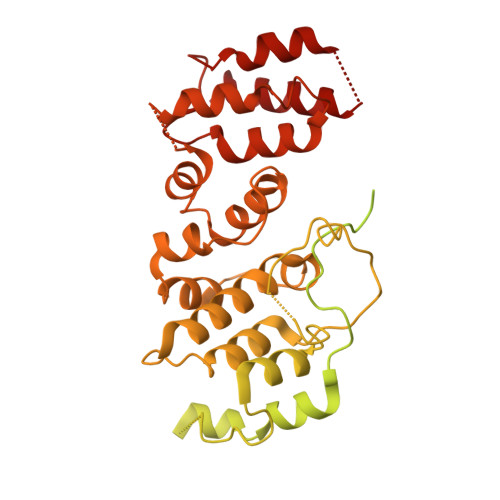
Integrative analysis reveals unique structural and functional features of the Smc5/6 complex.
Yu, Y., Li, S., Ser, Z., Sanyal, T., Choi, K., Wan, B., Kuang, H., Sali, A., Kentsis, A., Patel, D.J., Zhao, X.(2021) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 118
- PubMed: 33941673
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2026844118
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7LTO, 9A19 - PubMed Abstract:
Structural maintenance of chromosomes (SMC) complexes are critical chromatin modulators. In eukaryotes, the cohesin and condensin SMC complexes organize chromatin, while the Smc5/6 complex directly regulates DNA replication and repair. The molecular basis for the distinct functions of Smc5/6 is poorly understood. Here, we report an integrative structural study of the budding yeast Smc5/6 holo-complex using electron microscopy, cross-linking mass spectrometry, and computational modeling. We show that the Smc5/6 complex possesses several unique features, while sharing some architectural characteristics with other SMC complexes. In contrast to arm-folded structures of cohesin and condensin, Smc5 and Smc6 arm regions do not fold back on themselves. Instead, these long filamentous regions interact with subunits uniquely acquired by the Smc5/6 complex, namely the Nse2 SUMO ligase and the Nse5/Nse6 subcomplex, with the latter also serving as a linchpin connecting distal parts of the complex. Our 3.0-Å resolution cryoelectron microscopy structure of the Nse5/Nse6 core further reveals a clasped-hand topology and a dimeric interface important for cell growth. Finally, we provide evidence that Nse5/Nse6 uses its SUMO-binding motifs to contribute to Nse2-mediated sumoylation. Collectively, our integrative study identifies distinct structural features of the Smc5/6 complex and functional cooperation among its coevolved unique subunits.
- Structural Biology Program, Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, NY 10065.
Organizational Affiliation: