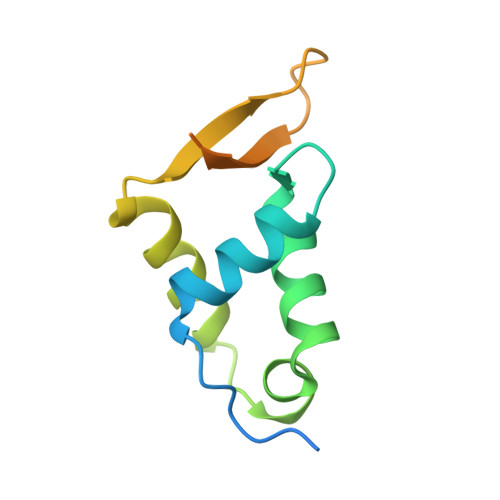
Mechanistic Insights into the Preference for Tandem Binding Sites in DNA Recognition by FOXM1.
Zhang, H., Dai, S., Liang, X., Li, J., Chen, Y.(2021) J Mol Biology 434: 167426-167426
- PubMed: 34973238
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2021.167426
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7FJ2 - PubMed Abstract:
FOXM1 is an essential proliferation-associated transcription factor that controls the activation of a number of cell cycle regulatory genes. Unlike other forkhead box (FOX) transcription factors, FOXM1 has been shown to prefer binding tandem regulatory DNA sites. However, the underlying reason for such preference is not clear. Here, we showed that the tandem DNA motif, named DIV2, is widely distributed in the promoter region of FOXM1 target genes. The binding of FOXM1 on the DIV2 site differs dramatically from other sites, which is in a highly cooperative fashion, with a much enhanced thermal stability and can be clearly detected by EMSA. The crystal structure of FOXM1 in complex with the DIV2 DNA reveals that the cooperative binding is likely to be driven by intermolecular protein-protein interactions (PPIs). Further half-site spacer insertion assays showed that FOXM1 can bind another site, DIV0, in a similar manner to the DIV2 site. Given the high occurrence of the DIV2 and DIV0 sites in FOXM1 target genes, our results suggest that FOXM1 prefers tandem DNA sites to enable cooperative DNA recognition, and such binding characteristics may further confer its specificity during transcriptional regulation.
- Department of Oncology, NHC Key Laboratory of Cancer Proteomics, Laboratory of Structural Biology, National Clinical Research Center for Geriatric Disorders, Xiangya Hospital, Central South University, Changsha, Hunan 410008, China.
Organizational Affiliation: