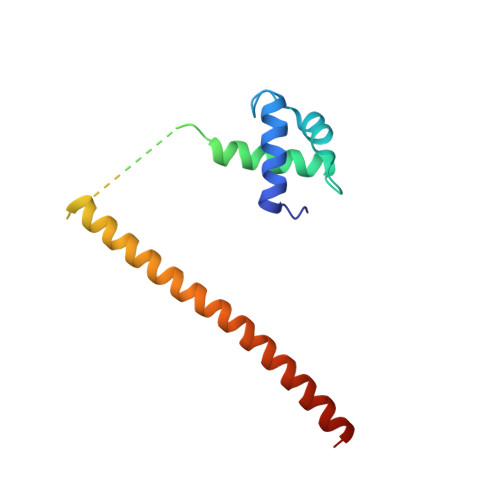
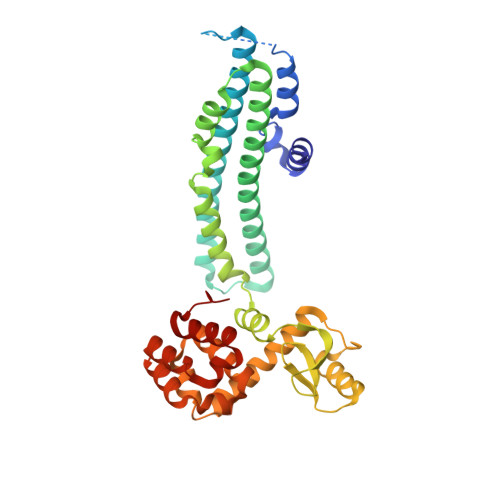
Mechanism of phosphate sensing and signaling revealed by rice SPX1-PHR2 complex structure.
Zhou, J., Hu, Q., Xiao, X., Yao, D., Ge, S., Ye, J., Li, H., Cai, R., Liu, R., Meng, F., Wang, C., Zhu, J.K., Lei, M., Xing, W.(2021) Nat Commun 12: 7040-7040
- PubMed: 34857773
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-27391-5
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7E40 - PubMed Abstract:
Phosphate, a key plant nutrient, is perceived through inositol polyphosphates (InsPs) by SPX domain-containing proteins. SPX1 an inhibit the PHR2 transcription factor to maintain Pi homeostasis. How SPX1 recognizes an InsP molecule and represses transcription activation by PHR2 remains unclear. Here we show that, upon binding InsP 6 , SPX1 can disrupt PHR2 dimers and form a 1:1 SPX1-PHR2 complex. The complex structure reveals that SPX1 helix α1 can impose a steric hindrance when interacting with the PHR2 dimer. By stabilizing helix α1, InsP 6 allosterically decouples the PHR2 dimer and stabilizes the SPX1-PHR2 interaction. In doing so, InsP 6 further allows SPX1 to engage with the PHR2 MYB domain and sterically block its interaction with DNA. Taken together, our results suggest that, upon sensing the surrogate signals of phosphate, SPX1 inhibits PHR2 via a dual mechanism that attenuates dimerization and DNA binding activities of PHR2.
- Shanghai Center for Plant Stress Biology and Center of Excellence in Molecular Plant Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai, 200032, China.
Organizational Affiliation: