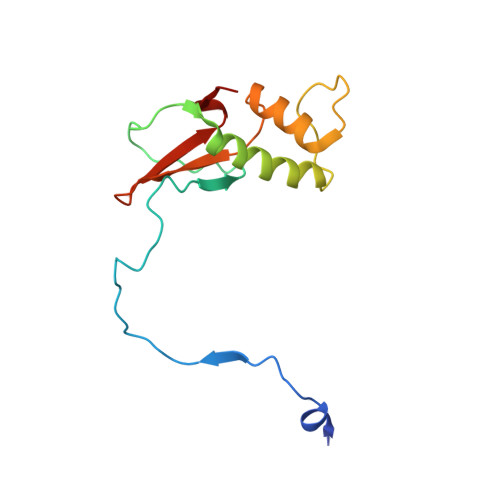
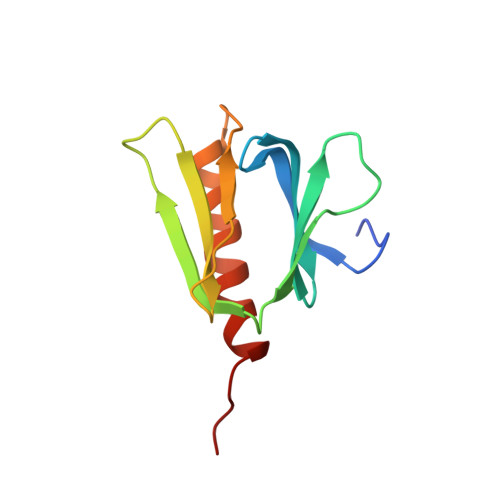
Three human RNA polymerases interact with TFIIH via a common RPB6 subunit.
Okuda, M., Suwa, T., Suzuki, H., Yamaguchi, Y., Nishimura, Y.(2022) Nucleic Acids Res 50: 1-16
- PubMed: 34268577
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkab612
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7DTH, 7DTI - PubMed Abstract:
In eukaryotes, three RNA polymerases (RNAPs) play essential roles in the synthesis of various types of RNA: namely, RNAPI for rRNA; RNAPII for mRNA and most snRNAs; and RNAPIII for tRNA and other small RNAs. All three RNAPs possess a short flexible tail derived from their common subunit RPB6. However, the function of this shared N-terminal tail (NTT) is not clear. Here we show that NTT interacts with the PH domain (PH-D) of the p62 subunit of the general transcription/repair factor TFIIH, and present the structures of RPB6 unbound and bound to PH-D by nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR). Using available cryo-EM structures, we modelled the activated elongation complex of RNAPII bound to TFIIH. We also provide evidence that the recruitment of TFIIH to transcription sites through the p62-RPB6 interaction is a common mechanism for transcription-coupled nucleotide excision repair (TC-NER) of RNAPI- and RNAPII-transcribed genes. Moreover, point mutations in the RPB6 NTT cause a significant reduction in transcription of RNAPI-, RNAPII- and RNAPIII-transcribed genes. These and other results show that the p62-RPB6 interaction plays multiple roles in transcription, TC-NER, and cell proliferation, suggesting that TFIIH is engaged in all RNAP systems.
- Graduate School of Medical Life Science, Yokohama City University, 1-7-29 Suehiro-cho, Tsurumi-ku, Yokohama 230-0045, Japan.
Organizational Affiliation: