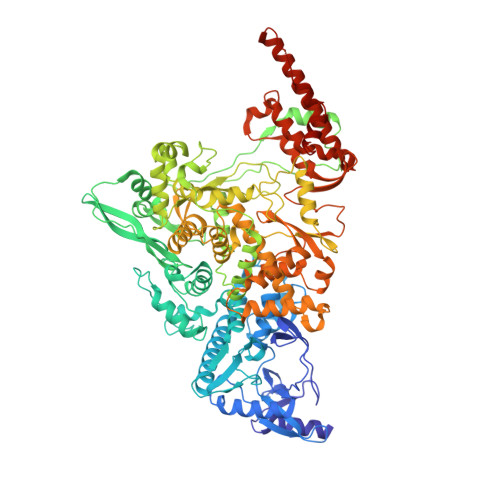
Structural Basis for RNA Replication by the SARS-CoV-2 Polymerase.
Wang, Q., Wu, J., Wang, H., Gao, Y., Liu, Q., Mu, A., Ji, W., Yan, L., Zhu, Y., Zhu, C., Fang, X., Yang, X., Huang, Y., Gao, H., Liu, F., Ge, J., Sun, Q., Yang, X., Xu, W., Liu, Z., Yang, H., Lou, Z., Jiang, B., Guddat, L.W., Gong, P., Rao, Z.(2020) Cell 182: 417-428.e13
- PubMed: 32526208
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2020.05.034
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7BZF, 7C2K - PubMed Abstract:
Nucleotide analog inhibitors, including broad-spectrum remdesivir and favipiravir, have shown promise in in vitro assays and some clinical studies for COVID-19 treatment, this despite an incomplete mechanistic understanding of the viral RNA-dependent RNA polymerase nsp12 drug interactions. Here, we examine the molecular basis of SARS-CoV-2 RNA replication by determining the cryo-EM structures of the stalled pre- and post- translocated polymerase complexes. Compared with the apo complex, the structures show notable structural rearrangements happening to nsp12 and its co-factors nsp7 and nsp8 to accommodate the nucleic acid, whereas there are highly conserved residues in nsp12, positioning the template and primer for an in-line attack on the incoming nucleotide. Furthermore, we investigate the inhibition mechanism of the triphosphate metabolite of remdesivir through structural and kinetic analyses. A transition model from the nsp7-nsp8 hexadecameric primase complex to the nsp12-nsp7-nsp8 polymerase complex is also proposed to provide clues for the understanding of the coronavirus transcription and replication machinery.
- Shanghai Institute for Advanced Immunochemical Studies and School of Life Science and Technology, ShanghaiTech University, Shanghai, China. Electronic address: wangq@shanghaitech.edu.cn.
Organizational Affiliation: