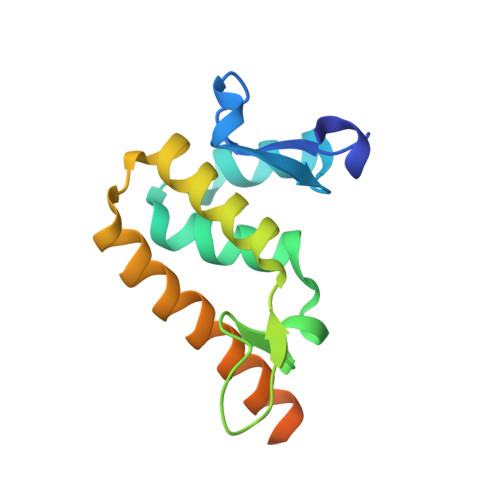
Structural insights into DNA recognition by the BEN domain of the transcription factor BANP.
Liu, K., Zhang, J., Xiao, Y., Yang, A., Song, X., Li, Y., Chen, Y., Hughes, T.R., Min, J.(2023) J Biological Chem 299: 104734-104734
- PubMed: 37086783
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbc.2023.104734
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7YUG, 7YUK, 7YUL, 7YUN, 8HTX - PubMed Abstract:
The BEN domain-containing transcription factors regulate transcription by recruiting chromatin-modifying factors to specific chromatin regions via their DNA-binding BEN domains. The BEN domain of BANP has been shown to bind to a CGCG DNA sequence or an AAA-containing matrix attachment regions DNA sequence. Consistent with these in vivo observations, we identified an optimal DNA-binding sequence of AAATCTCG by protein binding microarray, which was also confirmed by our isothermal titration calorimetry and mutagenesis results. We then determined crystal structures of the BANP BEN domain in apo form and in complex with a CGCG-containing DNA, respectively, which revealed that the BANP BEN domain mainly used the electrostatic interactions to bind DNA with some base-specific interactions with the TC motifs. Our isothermal titration calorimetry results also showed that BANP bound to unmethylated and methylated DNAs with comparable binding affinities. Our complex structure of BANP-mCGCG revealed that the BANP BEN domain bound to the unmethylated and methylated DNAs in a similar mode and cytosine methylation did not get involved in binding, which is also consistent with our observations from the complex structures of the BEND6 BEN domain with the CGCG or CGmCG DNAs. Taken together, our results further elucidate the elements important for DNA recognition and transcriptional regulation by the BANP BEN domain-containing transcription factor.
- Hubei Key Laboratory of Genetic Regulation and Integrative Biology, School of Life Sciences, Central China Normal University, Wuhan, PR China. Electronic address: keliu2015@ccnu.edu.cn.
Organizational Affiliation: