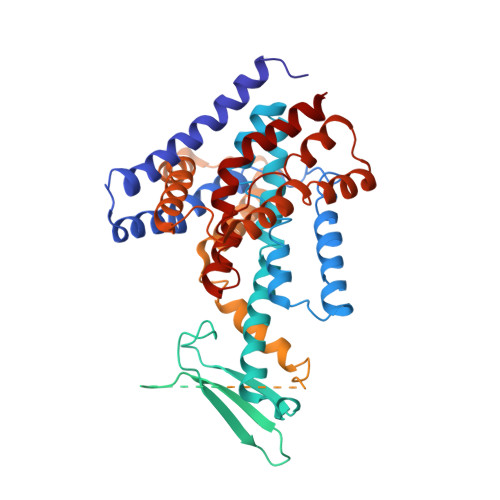
Structural insights into auxin recognition and efflux by Arabidopsis PIN1.
Yang, Z., Xia, J., Hong, J., Zhang, C., Wei, H., Ying, W., Sun, C., Sun, L., Mao, Y., Gao, Y., Tan, S., Friml, J., Li, D., Liu, X., Sun, L.(2022) Nature 609: 611-615
- PubMed: 35917925
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-022-05143-9
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7Y9T, 7Y9U, 7Y9V - PubMed Abstract:
Polar auxin transport is unique to plants and coordinates their growth and development 1,2 . The PIN-FORMED (PIN) auxin transporters exhibit highly asymmetrical localizations at the plasma membrane and drive polar auxin transport 3,4 ; however, their structures and transport mechanisms remain largely unknown. Here, we report three inward-facing conformation structures of Arabidopsis thaliana PIN1: the apo state, bound to the natural auxin indole-3-acetic acid (IAA), and in complex with the polar auxin transport inhibitor N-1-naphthylphthalamic acid (NPA). The transmembrane domain of PIN1 shares a conserved NhaA fold 5 . In the substrate-bound structure, IAA is coordinated by both hydrophobic stacking and hydrogen bonding. NPA competes with IAA for the same site at the intracellular pocket, but with a much higher affinity. These findings inform our understanding of the substrate recognition and transport mechanisms of PINs and set up a framework for future research on directional auxin transport, one of the most crucial processes underlying plant development.
- The First Affiliated Hospital of USTC, MOE Key Laboratory for Membraneless Organelles and Cellular Dynamics, Hefei National Laboratory for Physical Sciences at the Microscale, School of Life Sciences, Division of Life Sciences and Medicine, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, China.
Organizational Affiliation: