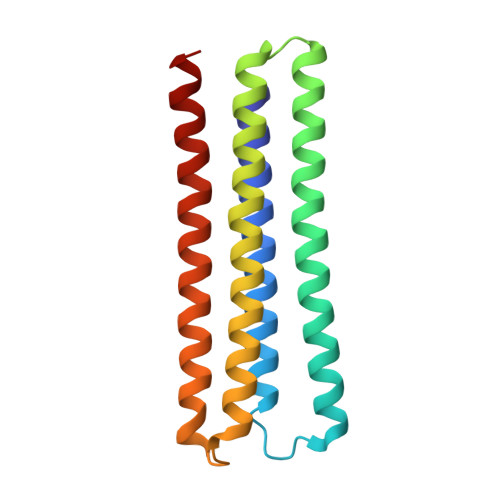
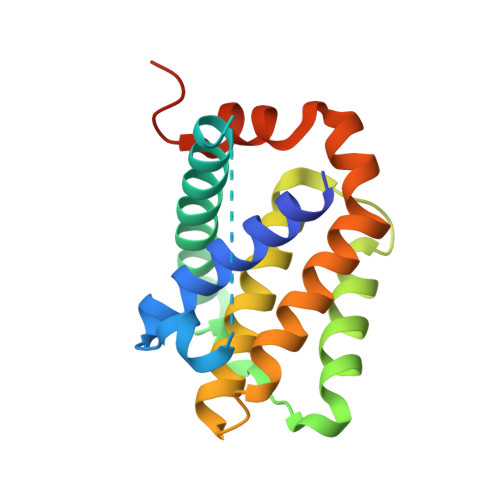
Computational design of an apoptogenic protein that binds BCL-xL and MCL-1 simultaneously and potently.
Kim, S., Park, H.S., Oh, B.H.(2022) Comput Struct Biotechnol J 20: 3019-3029
- PubMed: 35782728
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csbj.2022.06.021
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7XGE, 7XGF, 7XGG - PubMed Abstract:
One of the hallmarks of cancer cells is their ability to evade apoptosis, which confers survival advantages and resistance to anti-cancer drugs. Cancers often exhibit overexpression of anti-apoptotic BCL-2 proteins, the loss of which triggers apoptosis. In particular, the inhibition of both BCL-xL and MCL-1, but neither one individually, synergistically enhances apoptotic cell death. Here, we report computational design to produce a protein that inhibits both BCL-xL and MCL-1 simultaneously. To a reported artificial three-helix bundle whose second helix was designed to bind MCL-1, we added a fourth helix and designed it to bind BCL-xL. After structural validation of the design and further structure-based sequence design, we produced a dual-binding protein that interacts with both BCL-xL and MCL-1 with apparent dissociation constants of 820 pM and 196 pM, respectively. Expression of this dual binder in a subset of cancer cells induced apoptotic cell death at levels significantly higher than those induced by the pro-apoptotic BIM protein. With a genetic fusion of a mitochondria-targeting sequence or the BH3 sequence of BIM, the activity of the dual binder was enhanced even further. These data suggest that targeted delivery of this dual binder alone or as a part of a modular protein to cancers in the form of protein, mRNA, or DNA may be an effective way to induce cancer cell apoptosis.
- Department of Biological Sciences, KAIST Institute for the Biocentury, Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology, Daejeon 34141, Republic of Korea.
Organizational Affiliation: