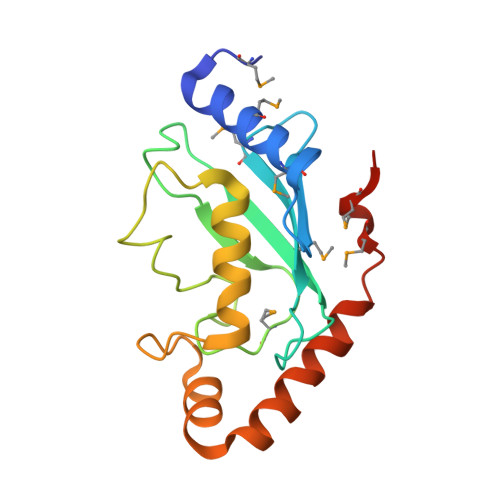
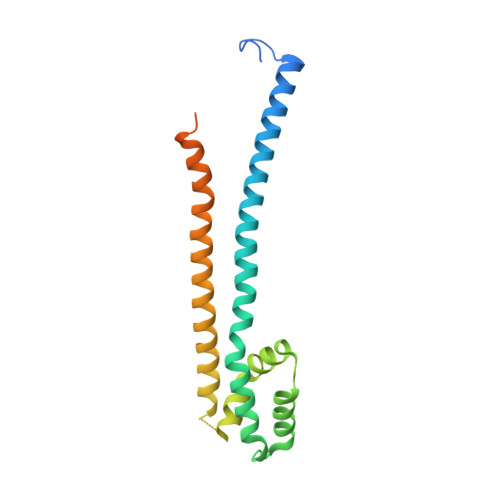
Structural basis for the Rad6 activation by the Bre1 N-terminal domain.
Shi, M., Zhao, J., Zhang, S., Huang, W., Li, M., Bai, X., Zhang, W., Zhang, K., Chen, X., Xiang, S.(2023) Elife 12
- PubMed: 36912886
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.84157
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7W75, 7W76 - PubMed Abstract:
The mono-ubiquitination of the histone protein H2B (H2Bub1) is a highly conserved histone post-translational modification that plays critical roles in many fundamental processes. In yeast, this modification is catalyzed by the conserved Bre1-Rad6 complex. Bre1 contains a unique N-terminal Rad6-binding domain (RBD), how it interacts with Rad6 and contributes to the H2Bub1 catalysis is unclear. Here, we present crystal structure of the Bre1 RBD-Rad6 complex and structure-guided functional studies. Our structure provides a detailed picture of the interaction between the dimeric Bre1 RBD and a single Rad6 molecule. We further found that the interaction stimulates Rad6's enzymatic activity by allosterically increasing its active site accessibility and likely contribute to the H2Bub1 catalysis through additional mechanisms. In line with these important functions, we found that the interaction is crucial for multiple H2Bub1-regulated processes. Our study provides molecular insights into the H2Bub1 catalysis.
- Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Key Laboratory of Immune Microenvironment and Disease (Ministry of Education), The province and ministry co-sponsored collaborative innovation center for medical epigenetics, Tianjin Medical University, Tianjin, China.
Organizational Affiliation: