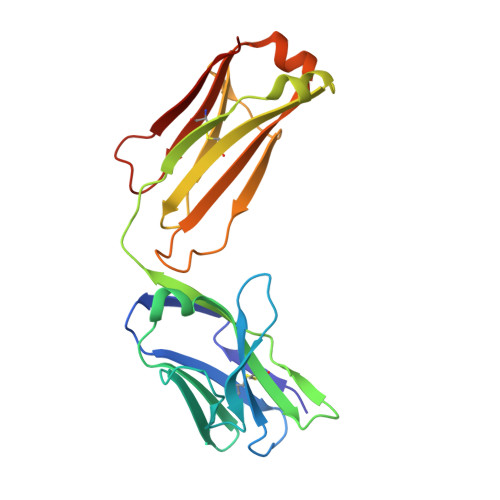
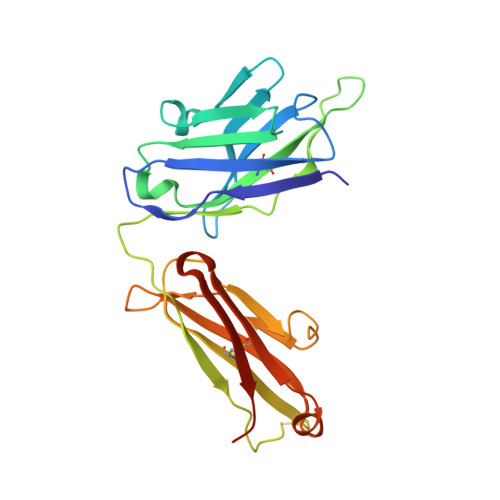
Antigenic mapping reveals sites of vulnerability on alpha-HCoV spike protein.
Xiang, J., Su, J., Lan, Q., Zhao, W., Zhou, Y., Xu, Y., Niu, J., Xia, S., Qi, Q., Sidhu, S., Lu, L., Miersch, S., Yang, B.(2022) Commun Biol 5: 1179-1179
- PubMed: 36333470
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s42003-022-04160-8
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7VMZ, 7VN9, 7VNG - PubMed Abstract:
Understanding the antigenic signatures of all human coronaviruses (HCoVs) Spike (S) proteins is imperative for pan-HCoV epitopes identification and broadly effective vaccine development. To depict the currently elusive antigenic signatures of α-HCoVs S proteins, we isolated a panel of antibodies against the HCoV-229E S protein and characterized their epitopes and neutralizing potential. We found that the N-terminal domain of HCoV-229E S protein is antigenically dominant wherein an antigenic supersite is present and appears conserved in HCoV-NL63, which holds potential to serve as a pan-α-HCoVs epitope. In the receptor binding domain, a neutralizing epitope is captured in the end distal to the receptor binding site, reminiscent of the locations of the SARS-CoV-2 RBD cryptic epitopes. We also identified a neutralizing antibody that recognizes the connector domain, thus representing the first S2-directed neutralizing antibody against α-HCoVs. The unraveled HCoVs S proteins antigenic similarities and variances among genera highlight the challenges faced by pan-HCoV vaccine design while supporting the feasibility of broadly effective vaccine development against a subset of HCoVs.
- School of Life Science and Technology and Shanghai Institute for Advanced Immunochemical Studies, ShanghaiTech University, 393 Middle Huaxia Road, 201210, Shanghai, China.
Organizational Affiliation: