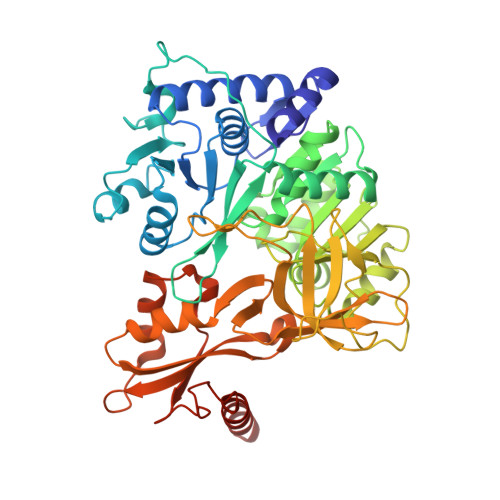
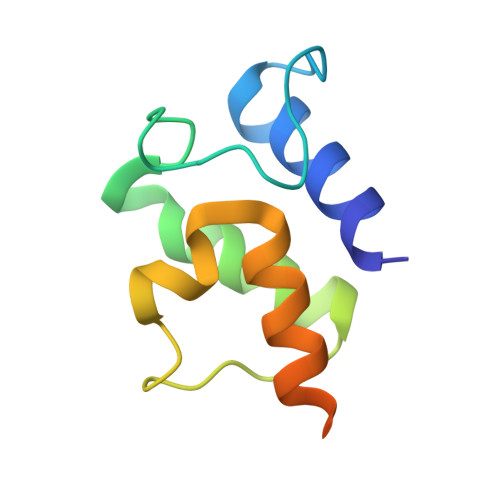
Essential Role of Loop Dynamics in Type II NRPS Biomolecular Recognition.
Corpuz, J.C., Patel, A., Davis, T.D., Podust, L.M., McCammon, J.A., Burkart, M.D.(2022) ACS Chem Biol 17: 2890-2898
- PubMed: 36173802
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acschembio.2c00523
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7THN, 7THQ - PubMed Abstract:
Non-ribosomal peptides play a critical role in the clinic as therapeutic agents. To access more chemically diverse therapeutics, non-ribosomal peptide synthetases (NRPSs) have been targeted for engineering through combinatorial biosynthesis; however, this has been met with limited success in part due to the lack of proper protein-protein interactions between non-cognate proteins. Herein, we report our use of chemical biology to enable X-ray crystallography, molecular dynamics (MD) simulations, and biochemical studies to elucidate binding specificities between peptidyl carrier proteins (PCPs) and adenylation (A) domains. Specifically, we determined X-ray crystal structures of a type II PCP crosslinked to its cognate A domain, PigG and PigI, and of PigG crosslinked to a non-cognate PigI homologue, PltF. The crosslinked PCP-A domain structures possess large protein-protein interfaces that predominantly feature hydrophobic interactions, with specific electrostatic interactions that orient the substrate for active site delivery. MD simulations of the PCP-A domain complexes and unbound PCP structures provide a dynamical evaluation of the transient interactions formed at PCP-A domain interfaces, which confirm the previously hypothesized role of a PCP loop as a crucial recognition element. Finally, we demonstrate that the interfacial interactions at the PCP loop 1 region can be modified to control PCP binding specificity through gain-of-function mutations. This work suggests that loop conformational preferences and dynamism account for improved shape complementary in the PCP-A domain interactions. Ultimately, these studies show how crystallographic, biochemical, and computational methods can be used to rationally re-engineer NRPSs for non-cognate interactions.
- Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry, University of California, San Diego, 9500 Gilman Drive, La Jolla, California 92093-0358, United States.
Organizational Affiliation: