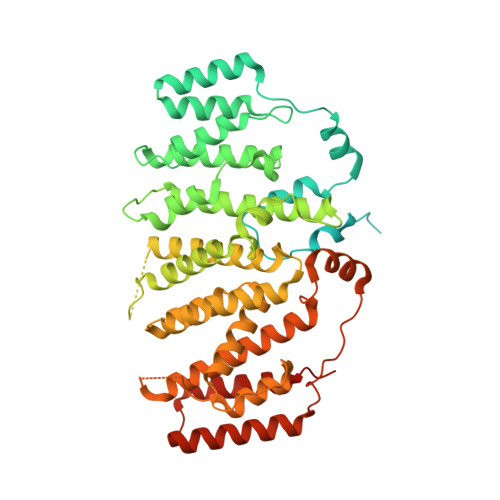
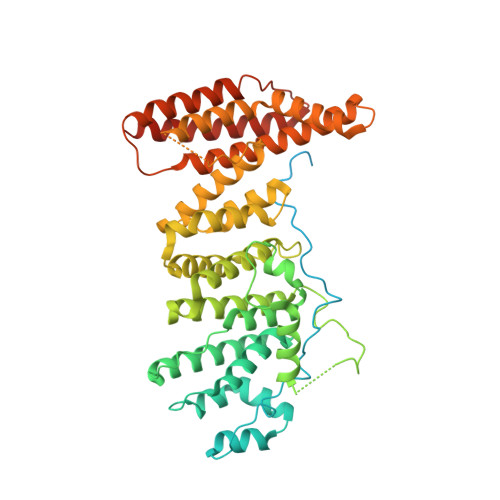
The Nse5/6-like SIMC1-SLF2 complex localizes SMC5/6 to viral replication centers.
Oravcova, M., Nie, M., Zilio, N., Maeda, S., Jami-Alahmadi, Y., Lazzerini-Denchi, E., Wohlschlegel, J.A., Ulrich, H.D., Otomo, T., Boddy, M.(2022) Elife 11
- PubMed: 36373674
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.79676
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7T5P - PubMed Abstract:
The human SMC5/6 complex is a conserved guardian of genome stability and an emerging component of antiviral responses. These disparate functions likely require distinct mechanisms of SMC5/6 regulation. In yeast, Smc5/6 is regulated by its Nse5/6 subunits, but such regulatory subunits for human SMC5/6 are poorly defined. Here, we identify a novel SMC5/6 subunit called SIMC1 that contains SUMO interacting motifs (SIMs) and an Nse5-like domain. We isolated SIMC1 from the proteomic environment of SMC5/6 within polyomavirus large T antigen (LT)-induced subnuclear compartments. SIMC1 uses its SIMs and Nse5-like domain to localize SMC5/6 to polyomavirus replication centers (PyVRCs) at SUMO-rich PML nuclear bodies. SIMC1's Nse5-like domain binds to the putative Nse6 orthologue SLF2 to form an anti-parallel helical dimer resembling the yeast Nse5/6 structure. SIMC1-SLF2 structure-based mutagenesis defines a conserved surface region containing the N-terminus of SIMC1's helical domain that regulates SMC5/6 localization to PyVRCs. Furthermore, SLF1, which recruits SMC5/6 to DNA lesions via its BRCT and ARD motifs, binds SLF2 analogously to SIMC1 and forms a separate Nse5/6-like complex. Thus, two Nse5/6-like complexes with distinct recruitment domains control human SMC5/6 localization.
- Department of Molecular Medicine, The Scripps Research Institute, La Jolla, United States.
Organizational Affiliation: