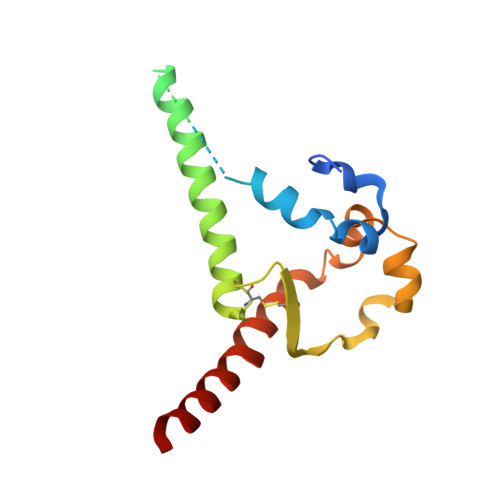
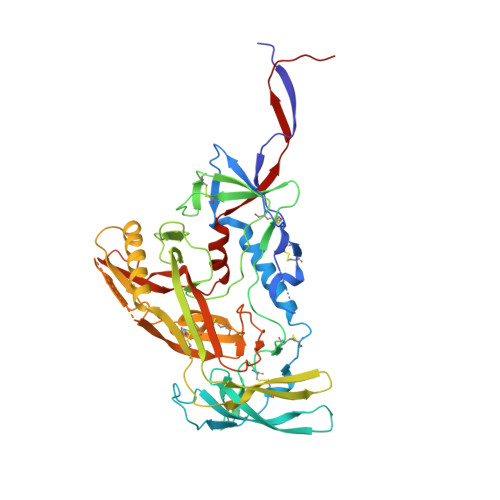
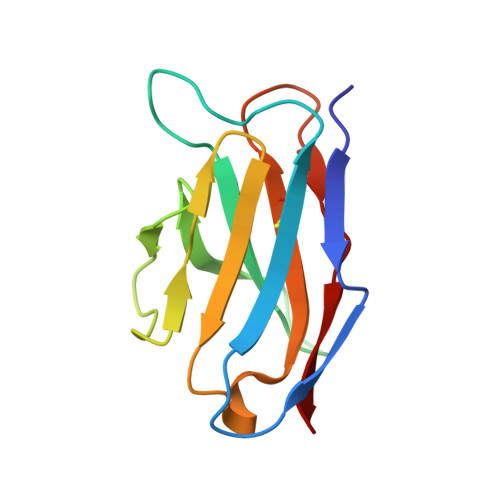
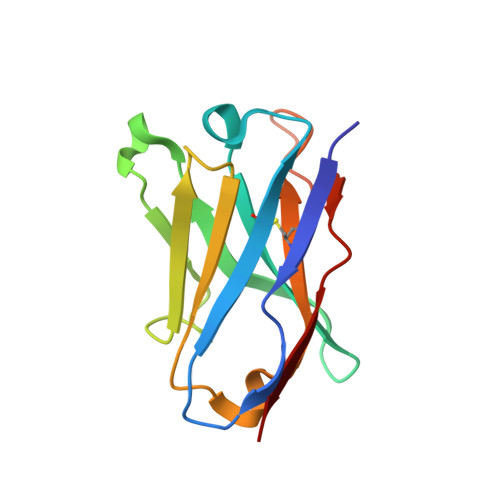
Induction of tier-2 neutralizing antibodies in mice with a DNA-encoded HIV envelope native like trimer.
Xu, Z., Walker, S., Wise, M.C., Chokkalingam, N., Purwar, M., Moore, A., Tello-Ruiz, E., Wu, Y., Majumdar, S., Konrath, K.M., Kulkarni, A., Tursi, N.J., Zaidi, F.I., Reuschel, E.L., Patel, I., Obeirne, A., Du, J., Schultheis, K., Gites, L., Smith, T., Mendoza, J., Broderick, K.E., Humeau, L., Pallesen, J., Weiner, D.B., Kulp, D.W.(2022) Nat Commun 13: 695-695
- PubMed: 35121758
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-28363-z
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7SQ1 - PubMed Abstract:
HIV Envelope (Env) is the main vaccine target for induction of neutralizing antibodies. Stabilizing Env into native-like trimer (NLT) conformations is required for recombinant protein immunogens to induce autologous neutralizing antibodies(nAbs) against difficult to neutralize HIV strains (tier-2) in rabbits and non-human primates. Immunizations of mice with NLTs have generally failed to induce tier-2 nAbs. Here, we show that DNA-encoded NLTs fold properly in vivo and induce autologous tier-2 nAbs in mice. DNA-encoded NLTs also uniquely induce both CD4 + and CD8 + T-cell responses as compared to corresponding protein immunizations. Murine neutralizing antibodies are identified with an advanced sequencing technology. The structure of an Env-Ab (C05) complex, as determined by cryo-EM, identifies a previously undescribed neutralizing Env C3/V5 epitope. Beyond potential functional immunity gains, DNA vaccines permit in vivo folding of structured antigens and provide significant cost and speed advantages for enabling rapid evaluation of new HIV vaccines.
- Vaccine and Immunotherapy Center, The Wistar Institute, Philadelphia, PA, 19104, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: