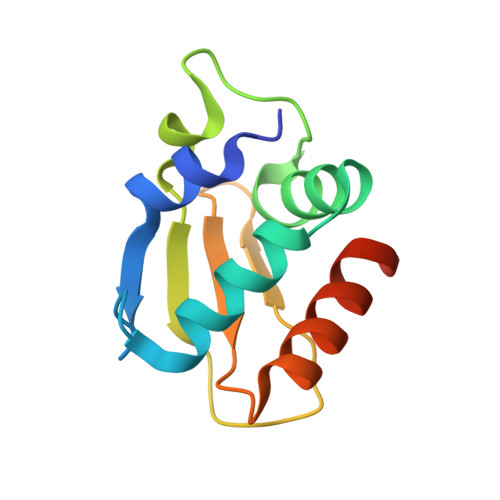
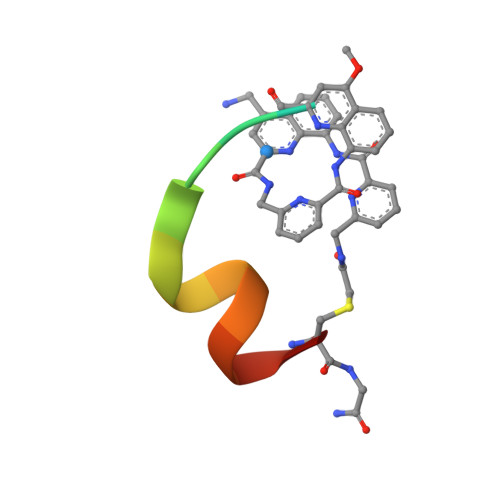
Display Selection of a Hybrid Foldamer-Peptide Macrocycle.
Dengler, S., Howard, R.T., Morozov, V., Tsiamantas, C., Huang, W.E., Liu, Z., Dobrzanski, C., Pophristic, V., Brameyer, S., Douat, C., Suga, H., Huc, I.(2023) Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 62: e202308408-e202308408
- PubMed: 37707879
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.202308408
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7QPB - PubMed Abstract:
Expanding the chemical diversity of peptide macrocycle libraries for display selection is desirable to improve their potential to bind biomolecular targets. We now have implemented a considerable expansion through a large aromatic helical foldamer inclusion. A foldamer was first identified that undergoes flexizyme-mediated tRNA acylation and that is capable of initiating ribosomal translation with yields sufficiently high to perform an mRNA display selection of macrocyclic foldamer-peptide hybrids. A hybrid macrocyclic nanomolar binder to the C-lobe of the E6AP HECT domain was selected that showed a highly converged peptide sequence. A crystal structure and molecular dynamics simulations revealed that both the peptide and foldamer are helical in an intriguing reciprocal stapling fashion. The strong residue convergence could be rationalized based on their involvement in specific interactions with the target protein. The foldamer stabilizes the peptide helix through stapling and through contacts with key residues. These results altogether represent a significant extension of the chemical space amenable to display selection and highlight possible benefits of inserting an aromatic foldamer into a peptide macrocycle for the purpose of protein recognition.
- Department of Pharmacy and Center for Integrated Protein Science, Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität, Butenandtstr. 5-13, 81377, München, Germany.
Organizational Affiliation: