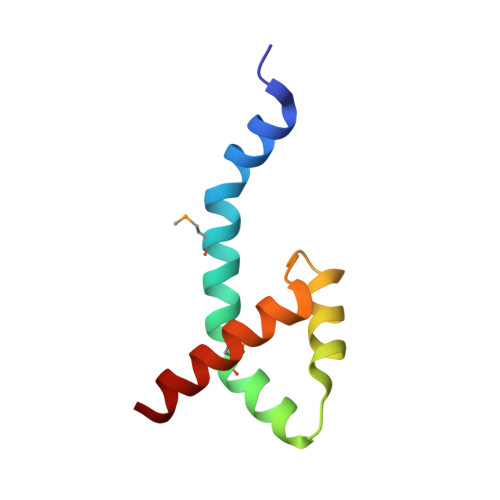
Characterization of the DNA Binding Domain of StbA, A Key Protein of A New Type of DNA Segregation System.
Quebre, V., Del Campo, I., Cuevas, A., Siguier, P., Rech, J., Le, P.T.N., Ton-Hoang, B., Cornet, F., Bouet, J.Y., Moncalian, G., de la Cruz, F., Guynet, C.(2022) J Mol Biology 434: 167752-167752
- PubMed: 35868361
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2022.167752
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7PC1 - PubMed Abstract:
Low-copy-number plasmids require sophisticated genetic devices to achieve efficient segregation of plasmid copies during cell division. Plasmid R388 uses a unique segregation mechanism, based on StbA, a small multifunctional protein. StbA is the key protein in a segregation system not involving a plasmid-encoded NTPase partner, it regulates the expression of several plasmid operons, and it is the main regulator of plasmid conjugation. The mechanisms by which StbA, together with the centromere-like sequence stbS, achieves segregation, is largely uncharacterized. To better understand the molecular basis of R388 segregation, we determined the crystal structure of the conserved N-terminal domain of StbA to 1.9 Å resolution. It folds into an HTH DNA-binding domain, structurally related to that of the PadR subfamily II of transcriptional regulators. StbA is organized in two domains. Its N-terminal domain carries the specific stbS DNA binding activity. A truncated version of StbA, deleted of its C-terminal domain, displays only partial activities in vivo, indicating that the non-conserved C-terminal domain is required for efficient segregation and subcellular plasmid positioning. The structure of StbA DNA-binding domain also provides some insight into how StbA monomers cooperate to repress transcription by binding to the stbDR and to form the segregation complex with stbS.
- Laboratoire de Microbiologie et de Génétique Moléculaires, Centre de Biologie Intégrative (CBI), Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique, Université de Toulouse, UPS, F-31000 Toulouse, France.
Organizational Affiliation: