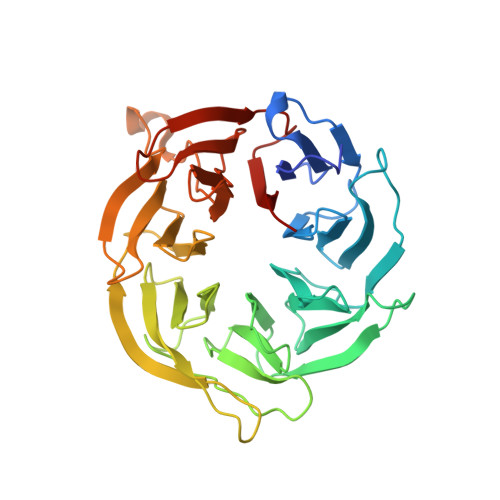
Bipartite binding and partial inhibition links DEPTOR and mTOR in a mutually antagonistic embrace.
Heimhalt, M., Berndt, A., Wagstaff, J., Anandapadamanaban, M., Perisic, O., Maslen, S., McLaughlin, S., Yu, C.W., Masson, G.R., Boland, A., Ni, X., Yamashita, K., Murshudov, G.N., Skehel, M., Freund, S.M., Williams, R.L.(2021) Elife 10
- PubMed: 34519269
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.68799
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7OWG - PubMed Abstract:
The mTORC1 kinase complex regulates cell growth, proliferation, and survival. Because mis-regulation of DEPTOR, an endogenous mTORC1 inhibitor, is associated with some cancers, we reconstituted mTORC1 with DEPTOR to understand its function. We find that DEPTOR is a unique partial mTORC1 inhibitor that may have evolved to preserve feedback inhibition of PI3K. Counterintuitively, mTORC1 activated by RHEB or oncogenic mutation is much more potently inhibited by DEPTOR. Although DEPTOR partially inhibits mTORC1, mTORC1 prevents this inhibition by phosphorylating DEPTOR, a mutual antagonism that requires no exogenous factors. Structural analyses of the mTORC1/DEPTOR complex showed DEPTOR's PDZ domain interacting with the mTOR FAT region, and the unstructured linker preceding the PDZ binding to the mTOR FRB domain. The linker and PDZ form the minimal inhibitory unit, but the N-terminal tandem DEP domains also significantly contribute to inhibition.
- MRC Laboratory of Molecular Biology, Cambridge, United Kingdom.
Organizational Affiliation: