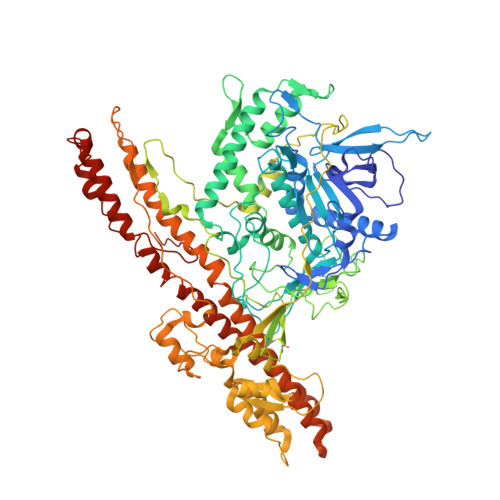
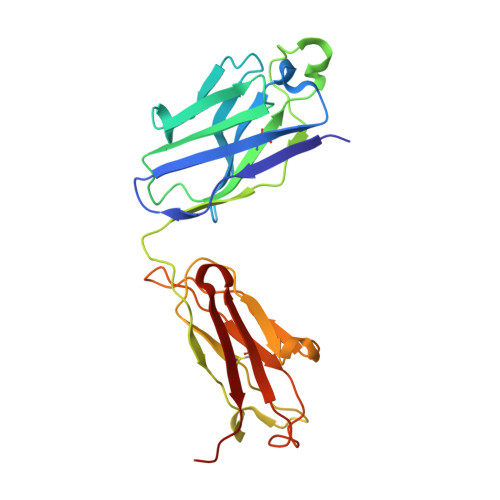
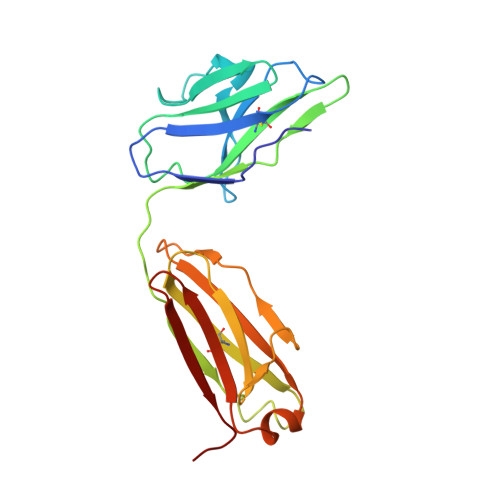
Exceptionally potent human monoclonal antibodies are effective for prophylaxis and treatment of tetanus in mice.
Pirazzini, M., Grinzato, A., Corti, D., Barbieri, S., Leka, O., Vallese, F., Tonellato, M., Silacci-Fregni, C., Piccoli, L., Kandiah, E., Schiavo, G., Zanotti, G., Lanzavecchia, A., Montecucco, C.(2021) J Clin Invest 131
- PubMed: 34618682
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI151676
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7OH0, 7OH1 - PubMed Abstract:
We used human monoclonal antibodies (humAbs) to study the mechanism of neuron intoxication by tetanus neurotoxin and to evaluate these antibodies as a safe preventive and therapeutic substitute for hyperimmune sera to treat tetanus in mice. By screening memory B cells from immune donors, we selected 2 tetanus neurotoxin-specific mAbs with exceptionally high neutralizing activities and extensively characterized them both structurally and functionally. We found that these antibodies interfered with the binding and translocation of the neurotoxin into neurons by interacting with 2 epitopes, whose identification pinpoints crucial events in the cellular pathogenesis of tetanus. Our observations explain the neutralization ability of these antibodies, which we found to be exceptionally potent in preventing experimental tetanus when injected into mice long before the toxin. Moreover, their Fab derivatives neutralized tetanus neurotoxin in post-exposure experiments, suggesting their potential for therapeutic use via intrathecal injection. As such, we believe these humAbs, as well as their Fab derivatives, meet the requirements to be considered for prophylactic and therapeutic use in human tetanus and are ready for clinical trials.
- Department of Biomedical Sciences, University of Padova, Padova, Italy.
Organizational Affiliation: