A novel class of Candida glabrata cell wall proteins with beta-helix fold mediates adhesion in clinical isolates.
Reithofer, V., Fernandez-Pereira, J., Alvarado, M., de Groot, P., Essen, L.O.(2021) PLoS Pathog 17: e1009980-e1009980
- PubMed: 34962966
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1009980
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
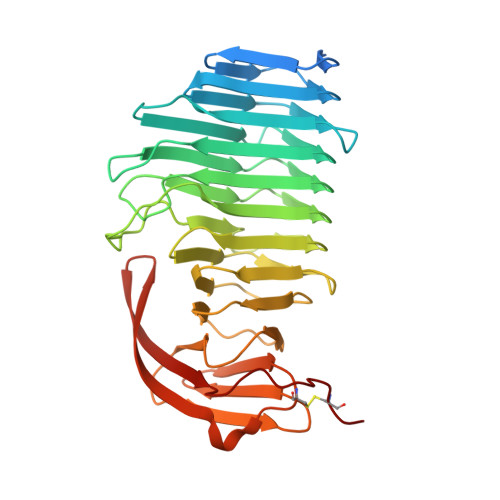
7O9O, 7O9P, 7O9Q - PubMed Abstract:
Candida glabrata is an opportunistic pathogenic yeast frequently causing infections in humans. Though it lacks typical virulence factors such as hyphal development, C. glabrata contains a remarkably large and diverse set of putative wall adhesins that is crucial for its success as pathogen. Here, we present an analysis of putative adhesins from the homology clusters V and VI. First, sequence similarity network analysis revealed relationships between cluster V and VI adhesins and S. cerevisiae haze protective factors (Hpf). Crystal structures of A-regions from cluster VI adhesins Awp1 and Awp3b reveal a parallel right-handed β-helix domain that is linked to a C-terminal β-sandwich. Structure solution of the A-region of Awp3b via single wavelength anomalous diffraction phasing revealed the largest known lanthanide cluster with 21 Gd3+ ions. Awp1-A and Awp3b-A show structural similarity to pectate lyases but binding to neither carbohydrates nor Ca2+ was observed. Phenotypic analysis of awp1Δ, awp3Δ, and awp1,3Δ double mutants did also not confirm their role as adhesins. In contrast, deletion mutants of the cluster V adhesin Awp2 in the hyperadhesive clinical isolate PEU382 demonstrated its importance for adhesion to polystyrene or glass, biofilm formation, cell aggregation and other cell surface-related phenotypes. Together with cluster III and VII adhesins our study shows that C. glabrata CBS138 can rely on a set of 42 Awp1-related adhesins with β-helix/α-crystallin domain architecture for modifying the surface characteristics of its cell wall.
- Department of Biochemistry, Philipps-Universität, Marburg, Germany.
Organizational Affiliation: