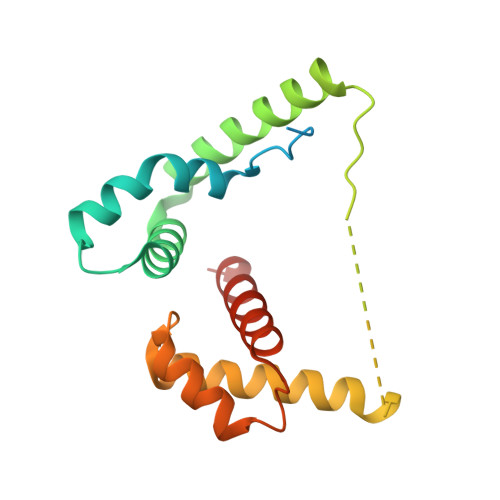
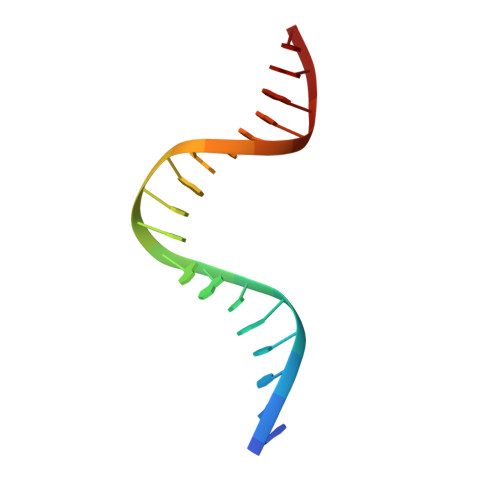
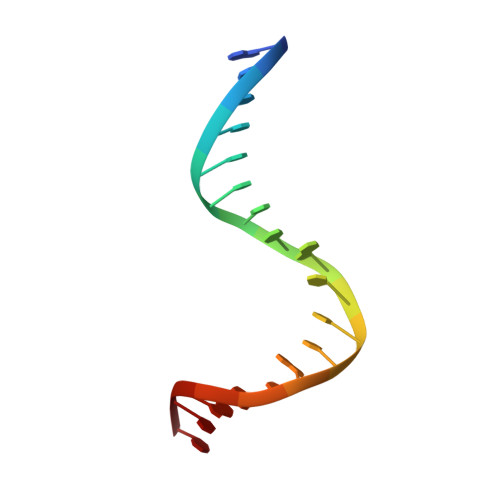
Molecular basis of DNA recognition by the HMG-box-C1 module of capicua.
Webb, J., Liew, J.J.M., Gnann, A.D., Ilkhani, K., Patterson, M., Paul, S., Fores, M., Jimenez, G., Veraksa, A., Dowling, D.P.(2025) Structure
- PubMed: 40967212
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2025.08.018
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7M5W - PubMed Abstract:
The HMG-box protein capicua (CIC) is a conserved transcriptional repressor with key functions in development and disease. CIC binding of DNA requires both its HMG-box and a separate domain called C1. How these domains cooperate to recognize specific DNA sequences is not known. Here, we report the crystal structure of the human CIC HMG-box and C1 domains complexed with a DNA oligomer containing a consensus octameric binding site. We find that both domains adopt tri-helical structures that pack against opposite sides of the DNA helix. The C1 domain folds into a helix-turn-helix (HTH) structure, inserting into the DNA major groove to enhance affinity. We investigate the system using molecular dynamics simulations and binding assays that interrogate the observed HMG-box and C1 domain interface and prominent cancer variants. Our results reveal a unique bipartite DNA-binding module and provide insights into the effects of cancer and domain interface mutations.
- Chemistry Department, University of Massachusetts Boston, Boston, MA 02125, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: