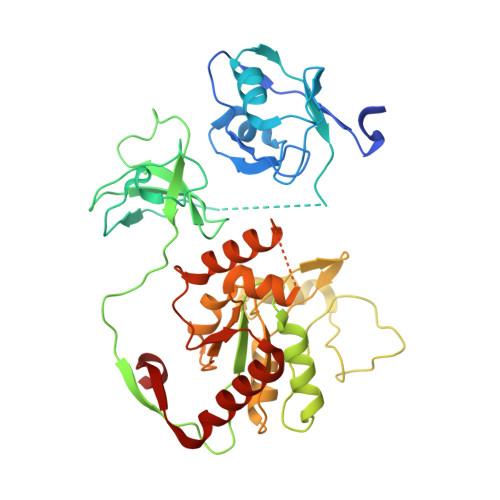
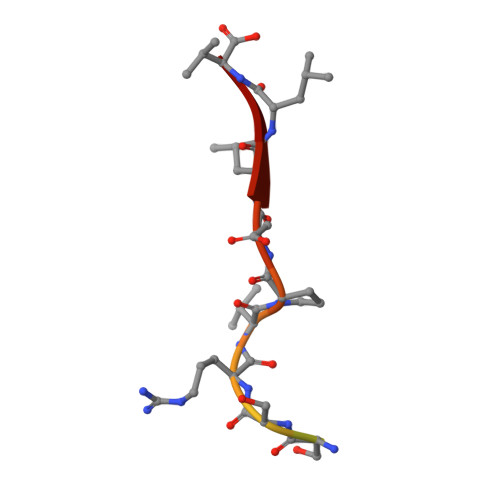
Structural basis for SARS-CoV-2 envelope protein recognition of human cell junction protein PALS1.
Chai, J., Cai, Y., Pang, C., Wang, L., McSweeney, S., Shanklin, J., Liu, Q.(2021) Nat Commun 12: 3433-3433
- PubMed: 34103506
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-23533-x
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7M4R - PubMed Abstract:
The COVID-19 pandemic, caused by the SARS-CoV-2 virus, has created global health and economic emergencies. SARS-CoV-2 viruses promote their own spread and virulence by hijacking human proteins, which occurs through viral protein recognition of human targets. To understand the structural basis for SARS-CoV-2 viral-host protein recognition, here we use cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) to determine a complex structure of the human cell junction protein PALS1 and SARS-CoV-2 viral envelope (E) protein. Our reported structure shows that the E protein C-terminal DLLV motif recognizes a pocket formed exclusively by hydrophobic residues from the PDZ and SH3 domains of PALS1. Our structural analysis provides an explanation for the observation that the viral E protein recruits PALS1 from lung epithelial cell junctions. In addition, our structure provides novel targets for peptide- and small-molecule inhibitors that could block the PALS1-E interactions to reduce E-mediated virulence.
- Biology Department, Brookhaven National Laboratory, Upton, NY, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: