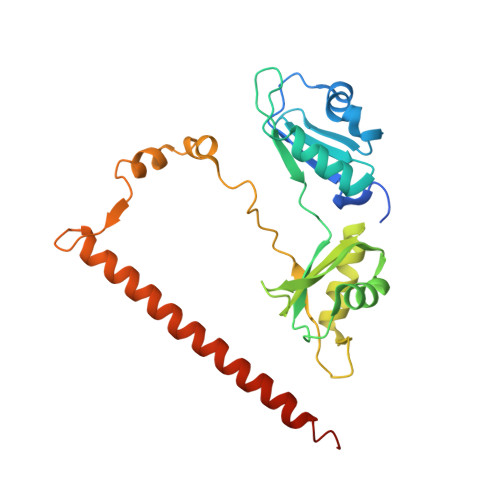
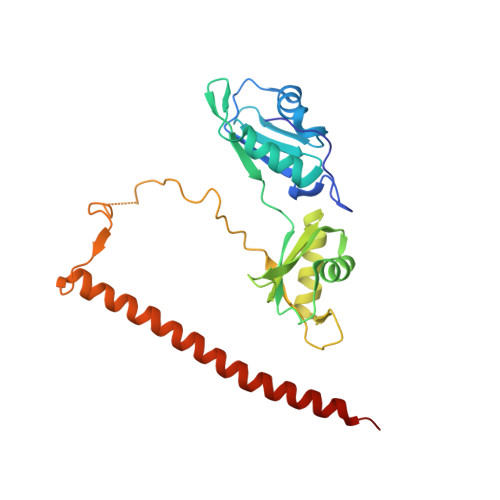
Paraspeckle subnuclear bodies depend on dynamic heterodimerisation of DBHS RNA-binding proteins via their structured domains.
Lee, P.W., Marshall, A.C., Knott, G.J., Kobelke, S., Martelotto, L., Cho, E., McMillan, P.J., Lee, M., Bond, C.S., Fox, A.H.(2022) J Biological Chem 298: 102563-102563
- PubMed: 36209820
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbc.2022.102563
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7LRQ - PubMed Abstract:
RNA-binding proteins of the DBHS (Drosophila Behavior Human Splicing) family, NONO, SFPQ, and PSPC1 have numerous roles in genome stability and transcriptional and posttranscriptional regulation. Critical to DBHS activity is their recruitment to distinct subnuclear locations, for example, paraspeckle condensates, where DBHS proteins bind to the long noncoding RNA NEAT1 in the first essential step in paraspeckle formation. To carry out their diverse roles, DBHS proteins form homodimers and heterodimers, but how this dimerization influences DBHS localization and function is unknown. Here, we present an inducible GFP-NONO stable cell line and use it for live-cell 3D-structured illumination microscopy, revealing paraspeckles with dynamic, twisted elongated structures. Using siRNA knockdowns, we show these labeled paraspeckles consist of GFP-NONO/endogenous SFPQ dimers and that GFP-NONO localization to paraspeckles depends on endogenous SFPQ. Using purified proteins, we confirm that partner swapping between NONO and SFPQ occurs readily in vitro. Crystallographic analysis of the NONO-SFPQ heterodimer reveals conformational differences to the other DBHS dimer structures, which may contribute to partner preference, RNA specificity, and subnuclear localization. Thus overall, our study suggests heterodimer partner availability is crucial for NONO subnuclear distribution and helps explain the complexity of both DBHS protein and paraspeckle dynamics through imaging and structural approaches.
- The School of Human Sciences, The University of Western Australia, Crawley, WA, Australia; The Harry Perkins Institute of Medical Research, QEII Medical Centre, Nedlands, and The Centre for Medical Research, The University of Western Australia, Crawley, WA, Australia.
Organizational Affiliation: