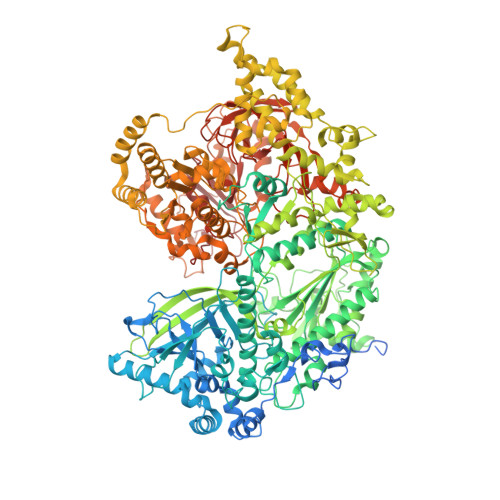
The large bat Helitron DNA transposase forms a compact monomeric assembly that buries and protects its covalently bound 5'-transposon end.
Kosek, D., Grabundzija, I., Lei, H., Bilic, I., Wang, H., Jin, Y., Peaslee, G.F., Hickman, A.B., Dyda, F.(2021) Mol Cell 81: 4271-4286.e4
- PubMed: 34403695
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2021.07.028
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7LCC - PubMed Abstract:
Helitrons are widespread eukaryotic DNA transposons that have significantly contributed to genome variability and evolution, in part because of their distinctive, replicative rolling-circle mechanism, which often mobilizes adjacent genes. Although most eukaryotic transposases form oligomers and use RNase H-like domains to break and rejoin double-stranded DNA (dsDNA), Helitron transposases contain a single-stranded DNA (ssDNA)-specific HUH endonuclease domain. Here, we report the cryo-electron microscopy structure of a Helitron transposase bound to the 5'-transposon end, providing insight into its multidomain architecture and function. The monomeric transposase forms a tightly packed assembly that buries the covalently attached cleaved end, protecting it until the second end becomes available. The structure reveals unexpected architectural similarity to TraI, a bacterial relaxase that also catalyzes ssDNA movement. The HUH active site suggests how two juxtaposed tyrosines, a feature of many replication initiators that use HUH nucleases, couple the conformational shift of an α-helix to control strand cleavage and ligation reactions.
- Laboratory of Molecular Biology, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD 20892, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: