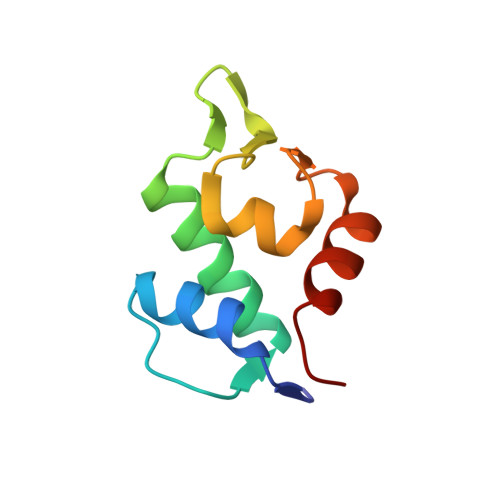
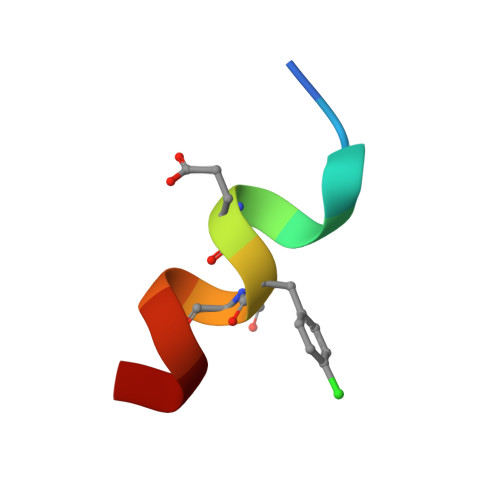A Dual-Specificity d-Peptide Antagonist of MDM2 and MDMX for Antitumor Immunotherapy.
Liao, C., Yan, J., Tolbert, W.D., Chen, X., Pazgier, M., Lu, W., Zhan, C., Lu, W.(2025) J Med Chem
- PubMed: 40824889
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.4c02057
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7KJM, 7KJN - PubMed Abstract:
Designing metabolically stable peptides to target interactions of the tumor suppressor protein p53 with the two oncogenic proteins MDM2 and MDMX represents an attractive approach to harvesting "high-hanging fruits" often inaccessible to traditional anticancer drug discovery and development efforts. Here, we report the design of a proteolysis-resistant d-dodecapeptide, termed D PMI-ω (EFWYVE p -ClFEKLLR), capable of disrupting the p53-MDM2/MDMX complex by antagonizing MDM2 and MDMX. D PMI-ω, upon fabrication on gold nanoparticles, efficiently traversed tumor cells and killed them by reactivating the p53 signaling pathway. Further, D PMI-ω inhibited B16 melanoma growth in vivo and, when combined with an anti-PD1 antibody, powerfully augmented the efficacy of immunotherapy by expanding CD3 + /CD8 + cytotoxic T cells and suppressing CD4 + /CD25 + regulatory T cells. Our work validates the design of a therapeutically viable anticancer peptide, showcasing its potential in combination therapy to treat patients with tumors that are otherwise resistant or poorly responsive to antitumor immunotherapy.
- Department of Clinical Pharmacology, Zhongshan Hospital, Fudan University, Shanghai 200032, China.
Organizational Affiliation: