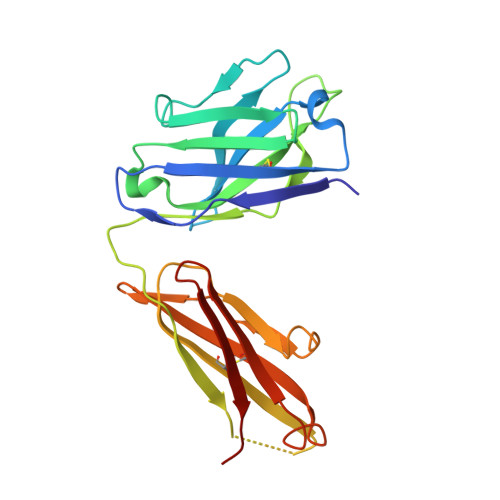
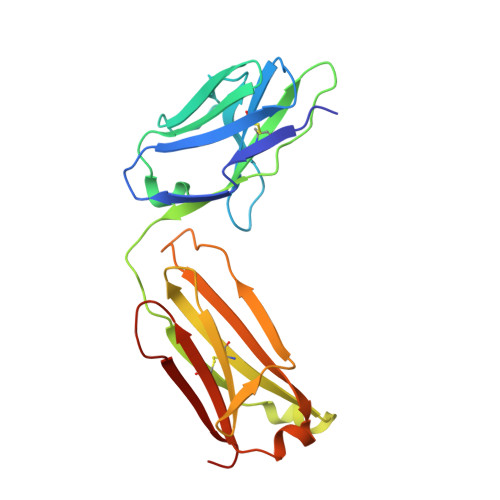
A Structural Model for the Ligand Binding of Pneumococcal Serotype 3 Capsular Polysaccharide-Specific Protective Antibodies.
Ozdilek, A., Huang, J., Babb, R., Paschall, A.V., Middleton, D.R., Duke, J.A., Pirofski, L.A., Mousa, J.J., Avci, F.Y.(2021) mBio 12: e0080021-e0080021
- PubMed: 34061603
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1128/mBio.00800-21
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7JVD - PubMed Abstract:
Capsular polysaccharides (CPSs) are major virulence factors that decorate the surfaces of many human bacterial pathogens. In their pure form or as glycoconjugate vaccines, CPSs are extensively used in vaccines deployed in clinical practice worldwide. However, our understanding of the structural requirements for interactions between CPSs and antibodies is limited. A longstanding model based on comprehensive observations of antibody repertoires binding to CPSs is that antibodies expressing heavy chain variable gene family 3 (VH3) predominate in these binding interactions in humans and VH3 homologs in mice. Toward understanding this highly conserved interaction, we generated a panel of mouse monoclonal antibodies (MAb) against Streptococcus pneumoniae serotype 3 CPS, determined an X-ray crystal structure of a protective MAb in complex with a hexasaccharide derived from enzymatic hydrolysis of the polysaccharide, and elucidated the structural requirements for this binding interaction. The crystal structure revealed a binding pocket containing aromatic side chains, suggesting the importance of hydrophobicity in the interaction. Through mutational analysis, we determined the amino acids that are critical in carbohydrate binding. Through elucidating the structural and functional properties of a panel of murine MAbs, we offer an explanation for the predominant use of the human VH3 gene family in antibodies against CPSs with implications in knowledge-based vaccine design. IMPORTANCE Infectious diseases caused by pathogenic bacteria are a major threat to human health. Capsular polysaccharides (CPSs) of many pathogenic bacteria have been used as the main components of glycoconjugate vaccines against bacterial diseases in clinical practice worldwide, with various degrees of success. Immunization with a glycoconjugate vaccine elicits T cell help for B cells that produce IgG antibodies to the CPS. Thus, it is important to develop an in-depth understanding of the interactions of carbohydrate epitopes with the antibodies. Structural characterization of the ligand binding of polysaccharide-specific antibodies laid out in this study may have fundamental biological implications for our comprehension of how the humoral immune system recognizes polysaccharide antigens, and in future knowledge-based vaccine design.
- Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, University of Georgia, Athens, Georgia, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: