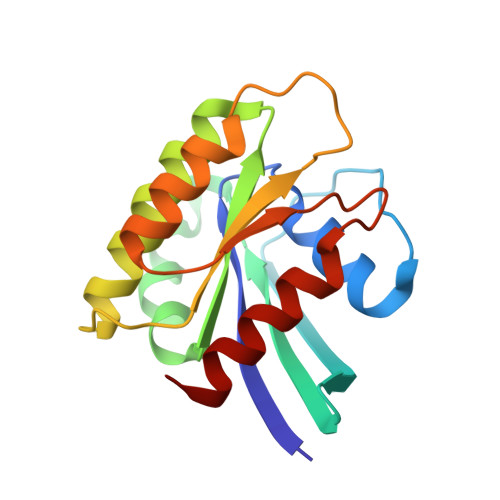
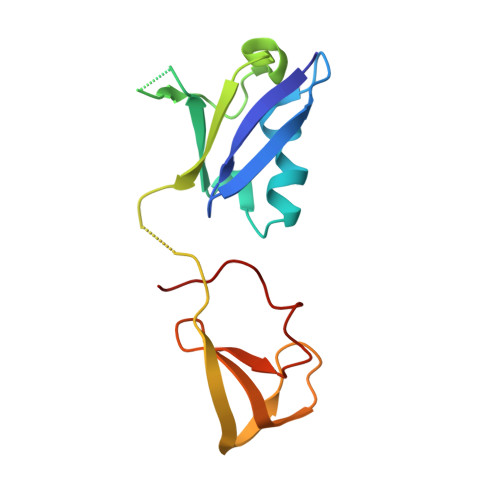
Crystal Structure Reveals the Full Ras-Raf Interface and Advances Mechanistic Understanding of Raf Activation.
Cookis, T., Mattos, C.(2021) Biomolecules 11
- PubMed: 34356620
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11070996
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7JHP - PubMed Abstract:
Ras and Raf-kinase interact through the Ras-binding (RBD) and cysteine-rich domains (CRD) of Raf to signal through the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway, yet the molecular mechanism leading to Raf activation has remained elusive. We present the 2.8 Å crystal structure of the HRas-CRaf-RBD_CRD complex showing the Ras-Raf interface as a continuous surface on Ras, as seen in the KRas-CRaf-RBD_CRD structure. In molecular dynamics simulations of a Ras dimer model formed through the α4-α5 interface, the CRD is dynamic and located between the two Ras protomers, poised for direct or allosteric modulation of functionally relevant regions of Ras and Raf. We propose a molecular model in which Ras binding is involved in the release of Raf autoinhibition while the Ras-Raf complex dimerizes to promote a platform for signal amplification, with Raf-CRD centrally located to impact regulation and function.
- Department of Chemistry and Chemical Biology, Northeastern University, Boston, MA 02115, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: