Structural insights into angiotensin receptor signaling modulation by balanced and biased agonists.
Zhang, D., Liu, Y., Zaidi, S.A., Xu, L., Zhan, Y., Chen, A., Guo, J., Huang, X.P., Roth, B.L., Katritch, V., Cherezov, V., Zhang, H.(2023) EMBO J 42: e112940-e112940
- PubMed: 37038975
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.15252/embj.2022112940
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7F6G - PubMed Abstract:
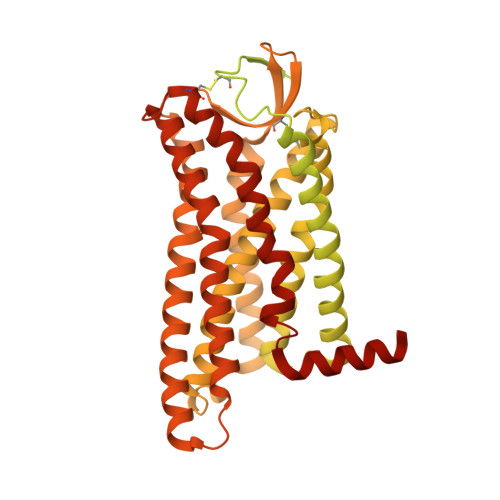
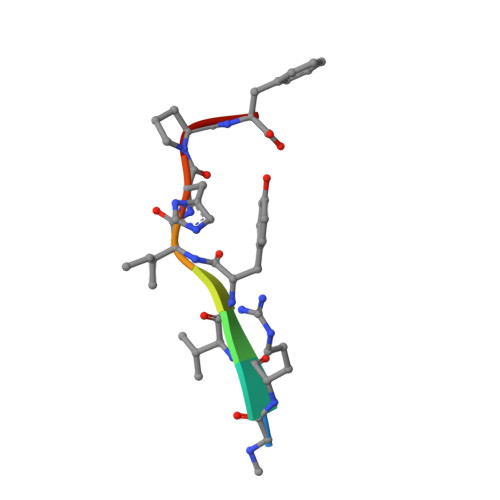
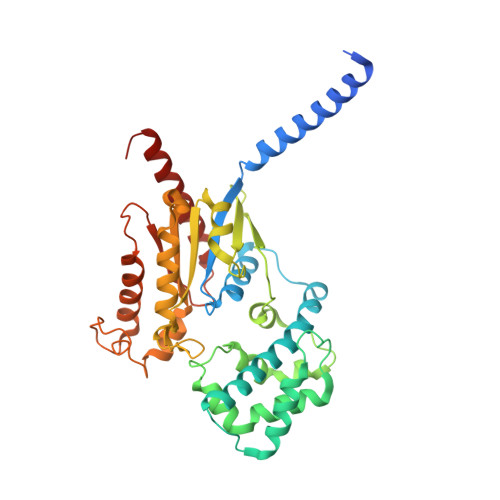
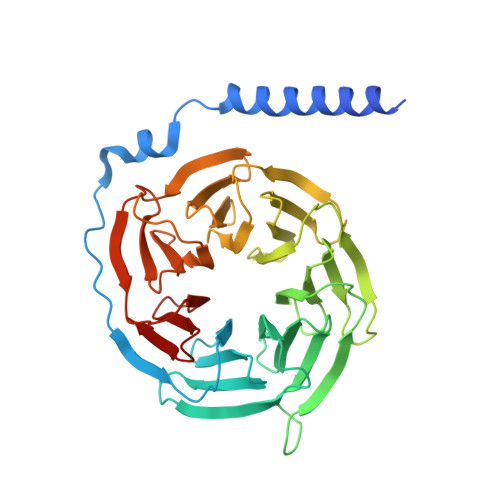
The peptide hormone angiotensin II regulates blood pressure mainly through the type 1 angiotensin II receptor AT 1 R and its downstream signaling proteins G q and β-arrestin. AT 1 R blockers, clinically used as antihypertensive drugs, inhibit both signaling pathways, whereas AT 1 R β-arrestin-biased agonists have shown great potential for the treatment of acute heart failure. Here, we present a cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) structure of the human AT 1 R in complex with a balanced agonist, Sar 1 -AngII, and G q protein at 2.9 Å resolution. This structure, together with extensive functional assays and computational modeling, reveals the molecular mechanisms for AT 1 R signaling modulation and suggests that a major hydrogen bond network (MHN) inside the receptor serves as a key regulator of AT 1 R signal transduction from the ligand-binding pocket to both G q and β-arrestin pathways. Specifically, we found that the MHN mutations N111 3.35 A and N294 7.45 A induce biased signaling to G q and β-arrestin, respectively. These insights should facilitate AT 1 R structure-based drug discovery for the treatment of cardiovascular diseases.
- Hangzhou Institute of Innovative Medicine, Institute of Pharmacology and Toxicology, Zhejiang Province Key Laboratory of Anti-Cancer Drug Research, College of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China.
Organizational Affiliation: