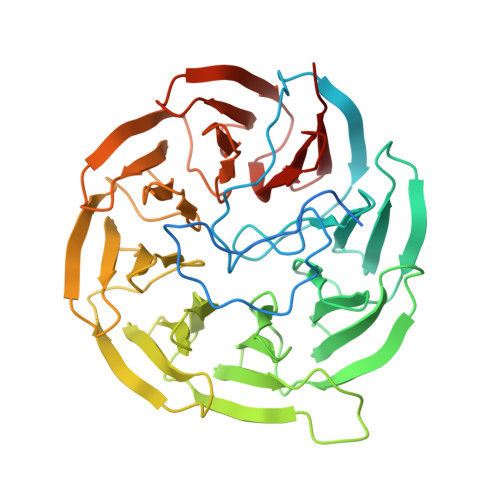
Structure of the plant growth-promoting factor YxaL from the rhizobacterium Bacillus velezensis and its application to protein engineering.
Kim, J., Pham, H., Baek, Y., Jo, I., Kim, Y.H., Ha, N.C.(2022) Acta Crystallogr D Struct Biol 78: 104-112
- PubMed: 34981766
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1107/S2059798321011724
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7DXN, 7EQ5, 7EVF - PubMed Abstract:
The YxaL protein was isolated from the soil bacterium Bacillus velezensis and has been shown to promote the root growth of symbiotic plants. YxaL has further been suggested to act as an exogenous signaling protein to induce the growth and branching of plant roots. Amino acid sequence analysis predicted YxaL to exhibit an eight-bladed β-propeller fold stabilized by six tryptophan-docking motifs and two modified motifs. Protein engineering to improve its structural stability is needed to increase the utility of YxaL as a plant growth-promoting factor. Here, the crystal structure of YxaL from B. velezensis was determined at 1.8 Å resolution to explore its structural features for structure-based protein engineering. The structure showed the typical eight-bladed β-propeller fold with structural variations in the third and fourth blades, which may decrease the stability of the β-propeller fold. Engineered proteins targeting the modified motifs were subsequently created. Crystal structures of the engineered YxaL proteins showed that the typical tryptophan-docking interaction was restored in the third and fourth blades, with increased structural stability, resulting in improved root growth-promoting activity in Arabidopsis seeds. The work is an example of structure-based protein engineering to improve the structural stability of β-propellor fold proteins.
- Department of Agricultural Biotechnology, Center for Food and Bioconvergence, and Research Institute of Agriculture and Life Sciences, CALS, Seoul National University, Seoul 08826, Republic of Korea.
Organizational Affiliation: