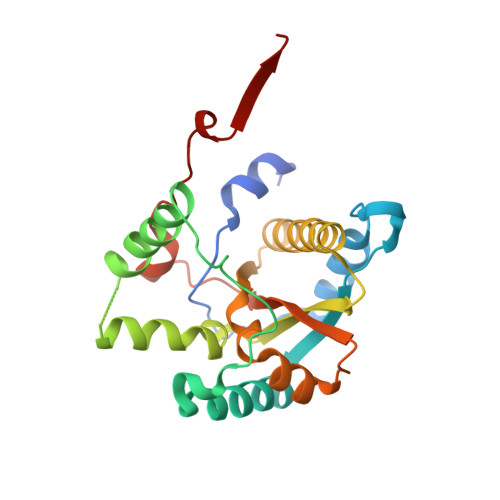
Structure and substrate specificity determinants of NfnB, a dinitroaniline herbicide-catabolizing nitroreductase from Sphingopyxis sp. strain HMH.
Kim, S.H., Park, S., Park, E., Kim, J.H., Ghatge, S., Hur, H.G., Rhee, S.(2021) J Biological Chem 297: 101143-101143
- PubMed: 34473996
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbc.2021.101143
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7DP0, 7DP1, 7DP2 - PubMed Abstract:
Nitroreductases are emerging as attractive bioremediation enzymes, with substrate promiscuity toward both natural and synthetic compounds. Recently, the nitroreductase NfnB from Sphingopyxis sp. strain HMH exhibited metabolic activity for dinitroaniline herbicides including butralin and pendimethalin, triggering the initial steps of their degradation and detoxification. However, the determinants of the specificity of NfnB for these herbicides are unknown. In this study, we performed structural and biochemical analyses of NfnB to decipher its substrate specificity. The homodimer NfnB is a member of the PnbA subgroup of the nitroreductase family. Each monomer displays a central α + β fold for the core domain, with a protruding middle region and an extended C-terminal region. The protruding middle region of Val75-Tyr129 represents a structural extension that is a common feature to members of the PnbA subgroup and functions as an opening wall connecting the coenzyme FMN-binding site to the surface, therefore serving as a substrate binding site. We performed mutational, kinetic, and structural analyses of mutant enzymes and found that Tyr88 in the middle region plays a pivotal role in substrate specificity by determining the dimensions of the wall opening. The mutation of Tyr88 to phenylalanine or alanine caused significant changes in substrate selectivity toward bulkier dinitroaniline herbicides such as oryzalin and isopropalin without compromising its activity. These results provide a framework to modify the substrate specificity of nitroreductase in the PnbA subgroup, which has been a challenging issue for its biotechnological and bioremediation applications.
- Department of Agricultural Biotechnology, Seoul National University, Seoul, Republic of Korea.
Organizational Affiliation: