Bicyclic beta-Sheet Mimetics that Target the Transcriptional Coactivator beta-Catenin and Inhibit Wnt Signaling.
Wendt, M., Bellavita, R., Gerber, A., Efrem, N.L., van Ramshorst, T., Pearce, N.M., Davey, P.R.J., Everard, I., Vazquez-Chantada, M., Chiarparin, E., Grieco, P., Hennig, S., Grossmann, T.N.(2021) Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 60: 13937-13944
- PubMed: 33783110
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.202102082
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7AR4 - PubMed Abstract:
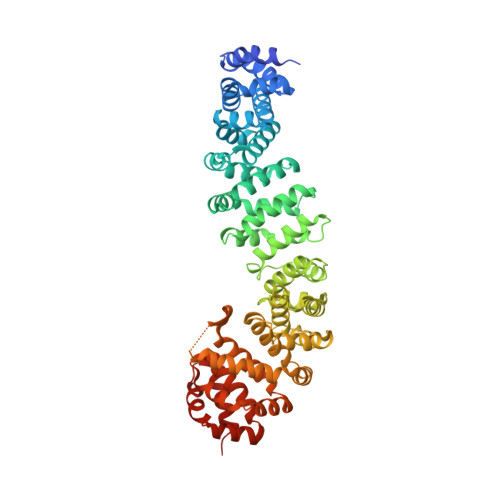
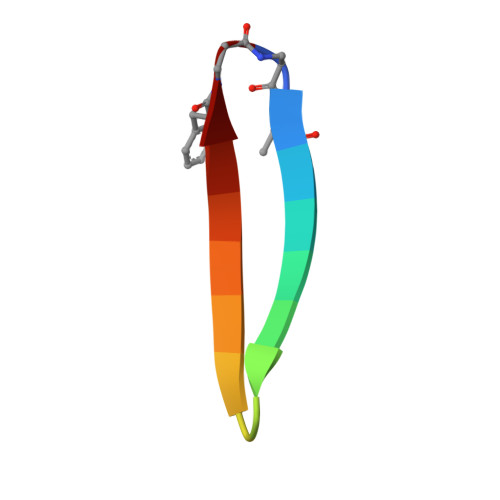
Protein complexes are defined by the three-dimensional structure of participating binding partners. Knowledge about these structures can facilitate the design of peptidomimetics which have been applied for example, as inhibitors of protein-protein interactions (PPIs). Even though β-sheets participate widely in PPIs, they have only rarely served as the basis for peptidomimetic PPI inhibitors, in particular when addressing intracellular targets. Here, we present the structure-based design of β-sheet mimetics targeting the intracellular protein β-catenin, a central component of the Wnt signaling pathway. Based on a protein binding partner of β-catenin, a macrocyclic peptide was designed and its crystal structure in complex with β-catenin obtained. Using this structure, we designed a library of bicyclic β-sheet mimetics employing a late-stage diversification strategy. Several mimetics were identified that compete with transcription factor binding to β-catenin and inhibit Wnt signaling in cells. The presented design strategy can support the development of inhibitors for other β-sheet-mediated PPIs.
- Department of Chemistry and Pharmaceutical Sciences, VU University Amsterdam, Amsterdam, The Netherlands.
Organizational Affiliation: