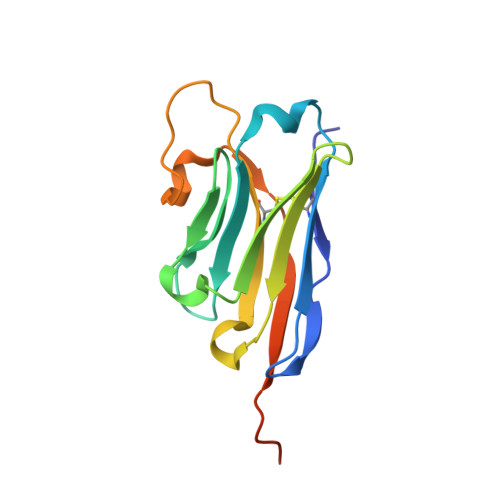
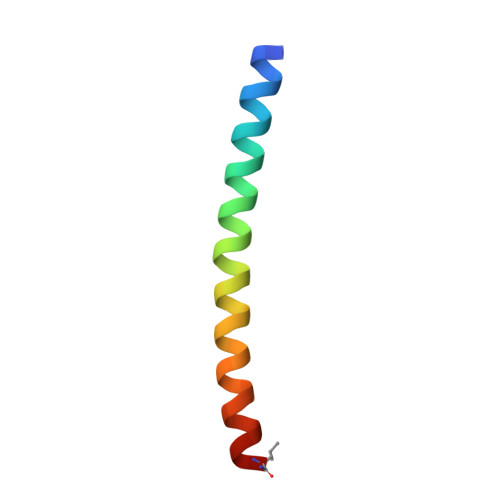
A nanobody toolbox targeting dimeric coiled-coil modules for functionalization of designed protein origami structures.
Majerle, A., Hadzi, S., Aupic, J., Satler, T., Lapenta, F., Strmsek, Z., Lah, J., Loris, R., Jerala, R.(2021) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 118
- PubMed: 33893235
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2021899118
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7A48, 7A4D, 7A4T, 7A4Y, 7A50 - PubMed Abstract:
Coiled-coil (CC) dimers are widely used in protein design because of their modularity and well-understood sequence-structure relationship. In CC protein origami design, a polypeptide chain is assembled from a defined sequence of CC building segments that determine the self-assembly of protein cages into polyhedral shapes, such as the tetrahedron, triangular prism, or four-sided pyramid. However, a targeted functionalization of the CC modules could significantly expand the versatility of protein origami scaffolds. Here, we describe a panel of single-chain camelid antibodies (nanobodies) directed against different CC modules of a de novo designed protein origami tetrahedron. We show that these nanobodies are able to recognize the same CC modules in different polyhedral contexts, such as isolated CC dimers, tetrahedra, triangular prisms, or trigonal bipyramids, thereby extending the ability to functionalize polyhedra with nanobodies in a desired stoichiometry. Crystal structures of five nanobody-CC complexes in combination with small-angle X-ray scattering show binding interactions between nanobodies and CC dimers forming the edges of a tetrahedron with the nanobody entering the tetrahedral cavity. Furthermore, we identified a pair of allosteric nanobodies in which the binding to the distant epitopes on the antiparallel homodimeric APH CC is coupled via a strong positive cooperativity. A toolbox of well-characterized nanobodies specific for CC modules provides a unique tool to target defined sites in the designed protein structures, thus opening numerous opportunities for the functionalization of CC protein origami polyhedra or CC-based bionanomaterials.
- Department of Synthetic Biology and Immunology, National Institute of Chemistry, SI-1000 Ljubljana, Slovenia.
Organizational Affiliation: