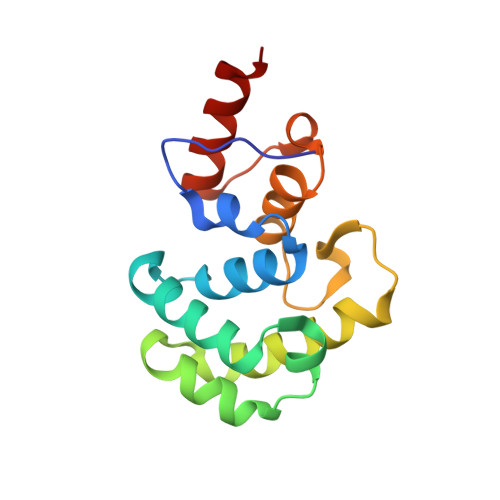
Catalytic mechanism of the mismatch-specific DNA glycosylase methyl-CpG-binding domain 4.
Ouzon-Shubeita, H., Jung, H., Lee, M.H., Koag, M.C., Lee, S.(2020) Biochem J 477: 1601-1612
- PubMed: 32297632
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1042/BCJ20200125
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6VJW - PubMed Abstract:
Thymine:guanine base pairs are major promutagenic mismatches occurring in DNA metabolism. If left unrepaired, these mispairs can cause C to T transition mutations. In humans, T:G mismatches are repaired in part by mismatch-specific DNA glycosylases such as methyl-CpG-binding domain 4 (hMBD4) and thymine-DNA glycosylase. Unlike lesion-specific DNA glycosylases, T:G-mismatch-specific DNA glycosylases specifically recognize both bases of the mismatch and remove the thymine but only from mispairs with guanine. Despite the advances in biochemical and structural characterizations of hMBD4, the catalytic mechanism of hMBD4 remains elusive. Herein, we report two structures of hMBD4 processing T:G-mismatched DNA. A high-resolution crystal structure of Asp560Asn hMBD4-T:G complex suggests that hMBD4-mediated glycosidic bond cleavage occurs via a general base catalysis mechanism assisted by Asp560. A structure of wild-type hMBD4 encountering T:G-containing DNA shows the generation of an apurinic/apyrimidinic (AP) site bearing the C1'-(S)-OH. The inversion of the stereochemistry at the C1' of the AP-site indicates that a nucleophilic water molecule approaches from the back of the thymine substrate, suggesting a bimolecular displacement mechanism (SN2) for hMBD4-catalyzed thymine excision. The AP-site is stabilized by an extensive hydrogen bond network in the MBD4 catalytic site, highlighting the role of MBD4 in protecting the genotoxic AP-site.
- Division of Chemical Biology and Medicinal Chemistry, College of Pharmacy, The University of Texas at Austin, Austin, TX 78712, U.S.A.
Organizational Affiliation: