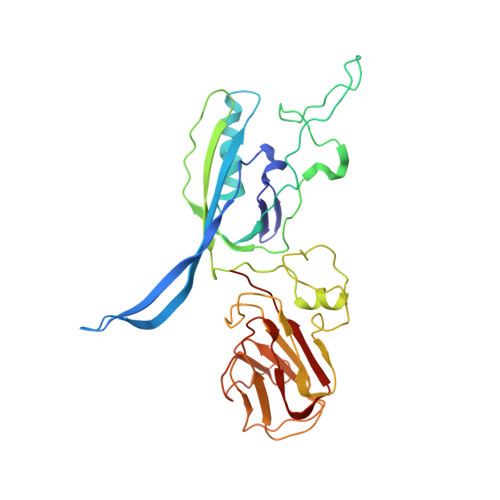
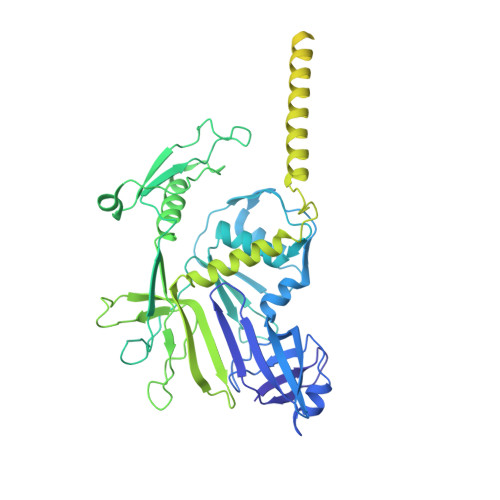
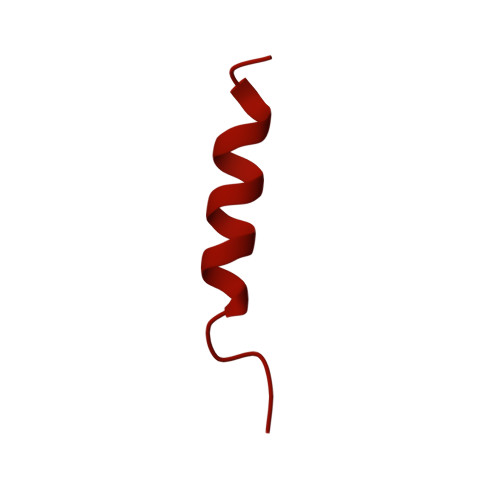
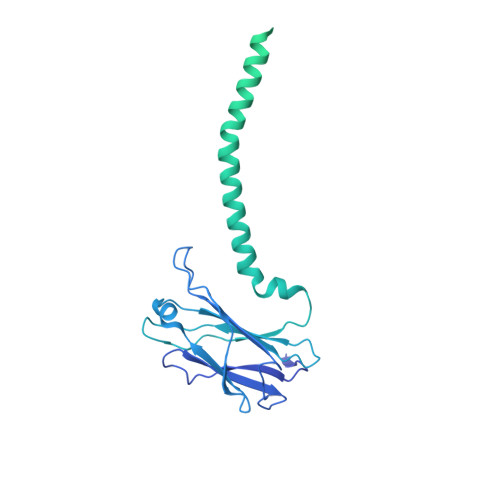
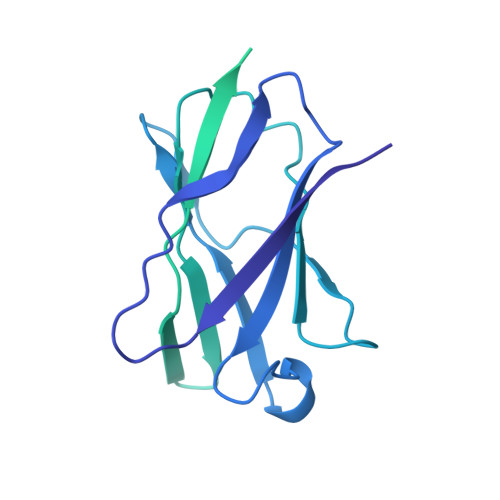
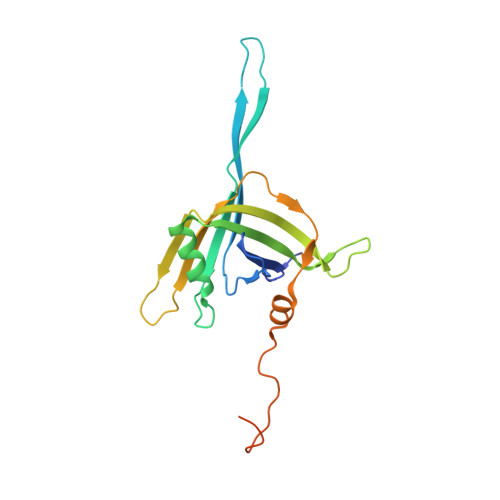
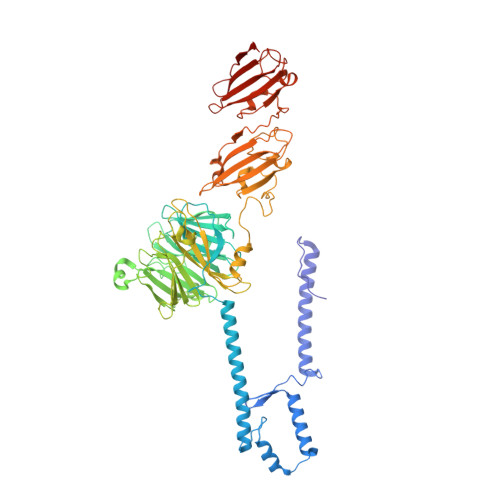
Structure of the host cell recognition and penetration machinery of a Staphylococcus aureus bacteriophage.
Kizziah, J.L., Manning, K.A., Dearborn, A.D., Dokland, T.(2020) PLoS Pathog 16: e1008314-e1008314
- PubMed: 32069326
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1008314
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6V8I - PubMed Abstract:
Staphylococcus aureus is a common cause of infections in humans. The emergence of virulent, antibiotic-resistant strains of S. aureus is a significant public health concern. Most virulence and resistance factors in S. aureus are encoded by mobile genetic elements, and transduction by bacteriophages represents the main mechanism for horizontal gene transfer. The baseplate is a specialized structure at the tip of bacteriophage tails that plays key roles in host recognition, cell wall penetration, and DNA ejection. We have used high-resolution cryo-electron microscopy to determine the structure of the S. aureus bacteriophage 80α baseplate at 3.75 Å resolution, allowing atomic models to be built for most of the major tail and baseplate proteins, including two tail fibers, the receptor binding protein, and part of the tape measure protein. Our structure provides a structural basis for understanding host recognition, cell wall penetration and DNA ejection in viruses infecting Gram-positive bacteria. Comparison to other phages demonstrates the modular design of baseplate proteins, and the adaptations to the host that take place during the evolution of staphylococci and other pathogens.
- Department of Microbiology, University of Alabama at Birmingham, Birmingham, Alabama, United States of America.
Organizational Affiliation: