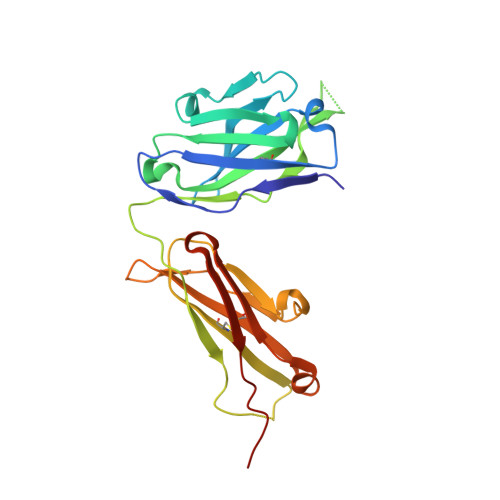
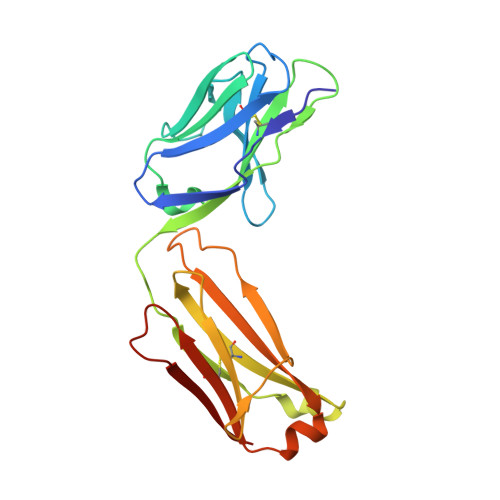
Hinge disulfides in human IgG2 CD40 antibodies modulate receptor signaling by regulation of conformation and flexibility.
Orr, C.M., Fisher, H., Yu, X., Chan, C.H., Gao, Y., Duriez, P.J., Booth, S.G., Elliott, I., Inzhelevskaya, T., Mockridge, I., Penfold, C.A., Wagner, A., Glennie, M.J., White, A.L., Essex, J.W., Pearson, A.R., Cragg, M.S., Tews, I.(2022) Sci Immunol 7: eabm3723-eabm3723
- PubMed: 35857577
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1126/sciimmunol.abm3723
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6TKB, 6TKC, 6TKD, 6TKE, 6TKF - PubMed Abstract:
Antibodies protect from infection, underpin successful vaccines and elicit therapeutic responses in otherwise untreatable cancers and autoimmune conditions. The human IgG2 isotype displays a unique capacity to undergo disulfide shuffling in the hinge region, leading to modulation of its ability to drive target receptor signaling (agonism) in a variety of important immune receptors, through hitherto unexplained molecular mechanisms. To address the underlying process and reveal how hinge disulfide orientation affects agonistic activity, we generated a series of cysteine to serine exchange variants in the hinge region of the clinically relevant monoclonal antibody ChiLob7/4, directed against the key immune receptor CD40. We report how agonistic activity varies with disulfide pattern and is afforded by the presence of a disulfide crossover between F(ab) arms in the agonistic forms, independently of epitope, as observed in the determined crystallographic structures. This structural "switch" affects directly on antibody conformation and flexibility. Small-angle x-ray scattering and ensemble modeling demonstrated that the least flexible variants adopt the fewest conformations and evoke the highest levels of receptor agonism. This covalent change may be amenable for broad implementation to modulate receptor signaling in an epitope-independent manner in future therapeutics.
- University of Southampton, Biological Sciences, Southampton SO17 1BJ, UK.
Organizational Affiliation: