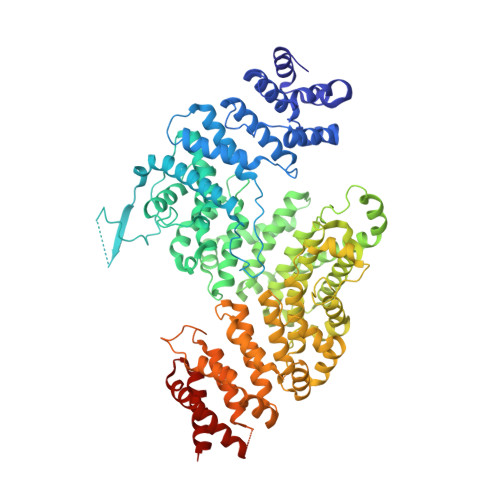
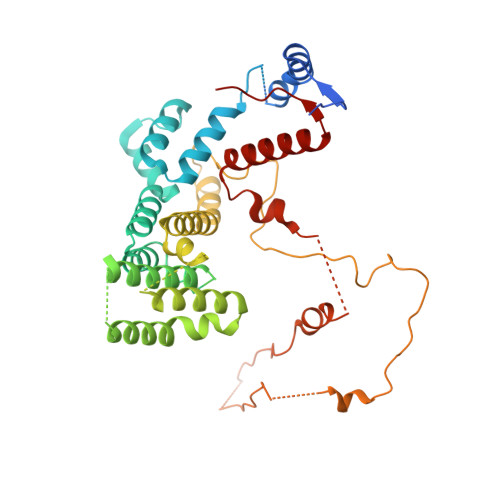
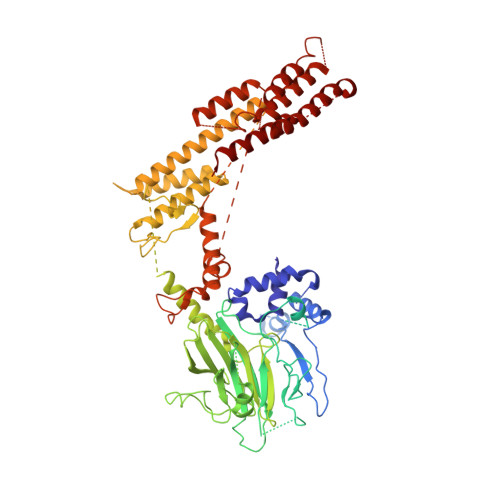
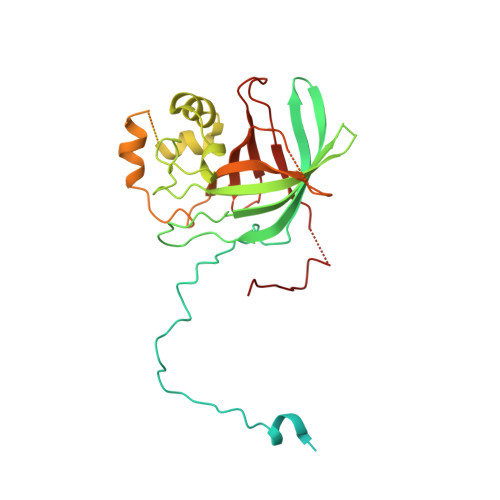
Interconversion between Anticipatory and Active GID E3 Ubiquitin Ligase Conformations via Metabolically Driven Substrate Receptor Assembly
Qiao, S., Langlois, C.R., Chrustowicz, J., Sherpa, D., Karayel, O., Hansen, F.M., Beier, V., von Gronau, S., Bollschweiler, D., Schafer, T., Alpi, A.F., Mann, M., Rajan Prabu, J., Schulman, B.A.(2020) Mol Cell 77: 1-14
- PubMed: 31708416
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2019.10.009
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6SWY - PubMed Abstract:
Cells respond to environmental changes by toggling metabolic pathways, preparing for homeostasis, and anticipating future stresses. For example, in Saccharomyces cerevisiae, carbon stress-induced gluconeogenesis is terminated upon glucose availability, a process that involves the multiprotein E3 ligase GID SR4 recruiting N termini and catalyzing ubiquitylation of gluconeogenic enzymes. Here, genetics, biochemistry, and cryoelectron microscopy define molecular underpinnings of glucose-induced degradation. Unexpectedly, carbon stress induces an inactive anticipatory complex (GID Ant ), which awaits a glucose-induced substrate receptor to form the active GID SR4 . Meanwhile, other environmental perturbations elicit production of an alternative substrate receptor assembling into a related E3 ligase complex. The intricate structure of GID Ant enables anticipating and ultimately binding various N-degron-targeting (i.e., "N-end rule") substrate receptors, while the GID SR4 E3 forms a clamp-like structure juxtaposing substrate lysines with the ubiquitylation active site. The data reveal evolutionarily conserved GID complexes as a family of multisubunit E3 ubiquitin ligases responsive to extracellular stimuli.
- Department of Molecular Machines and Signaling, Max Planck Institute of Biochemistry, 82152 Martinsried, Germany.
Organizational Affiliation: