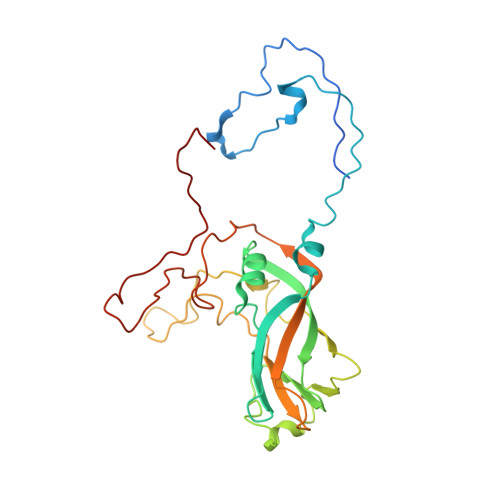
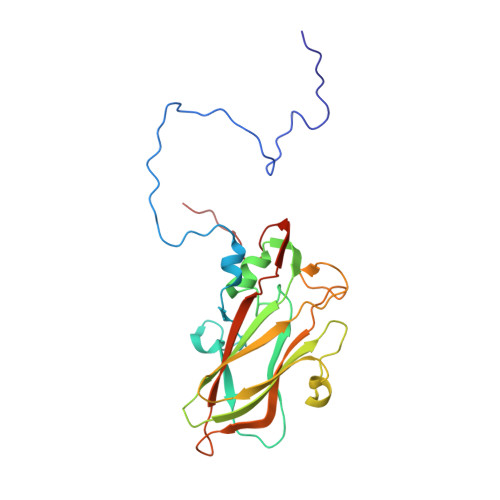
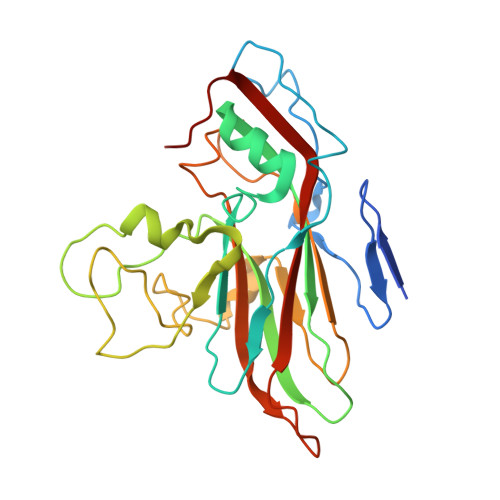
Cryo-EM structure of rhinovirus C15a bound to its cadherin-related protein 3 receptor.
Sun, Y., Watters, K., Hill, M.G., Fang, Q., Liu, Y., Kuhn, R.J., Klose, T., Rossmann, M.G., Palmenberg, A.C.(2020) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 117: 6784-6791
- PubMed: 32152109
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1921640117
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6PPO, 6PSF - PubMed Abstract:
Infection by Rhinovirus-C (RV-C), a species of Picornaviridae Enterovirus , is strongly associated with childhood asthma exacerbations. Cellular binding and entry by all RV-C, which trigger these episodes, is mediated by the first extracellular domain (EC1) of cadherin-related protein 3 (CDHR3), a surface cadherin-like protein expressed primarily on the apical surfaces of ciliated airway epithelial cells. Although recombinant EC1 is a potent inhibitor of viral infection, there is no molecular description of this protein or its binding site on RV-C. Here we present cryo-electron microscopy (EM) data resolving the EC1 and EC1+2 domains of human CDHR3 complexed with viral isolate C15a. Structure-suggested residues contributing to required interfaces on both EC1 and C15a were probed and identified by mutagenesis studies with four different RV-C genotypes. In contrast to most other rhinoviruses, which bind intercellular adhesion molecule 1 receptors via a capsid protein VP1-specific fivefold canyon feature, the CDHR3 EC1 contacts C15a, and presumably all RV-Cs, in a unique cohesive footprint near the threefold vertex, encompassing residues primarily from viral protein VP3, but also from VP1 and VP2. The EC1+2 footprint on C15a is similar to that of EC1 alone but shows that steric hindrance imposed by EC2 would likely prevent multiprotein binding by the native receptor at any singular threefold vertex. Definition of the molecular interface between the RV-Cs and their receptors provides new avenues that can be explored for potential antiviral therapies.
- Department of Biological Sciences, Purdue University, West Lafayette, IN 47907.
Organizational Affiliation: